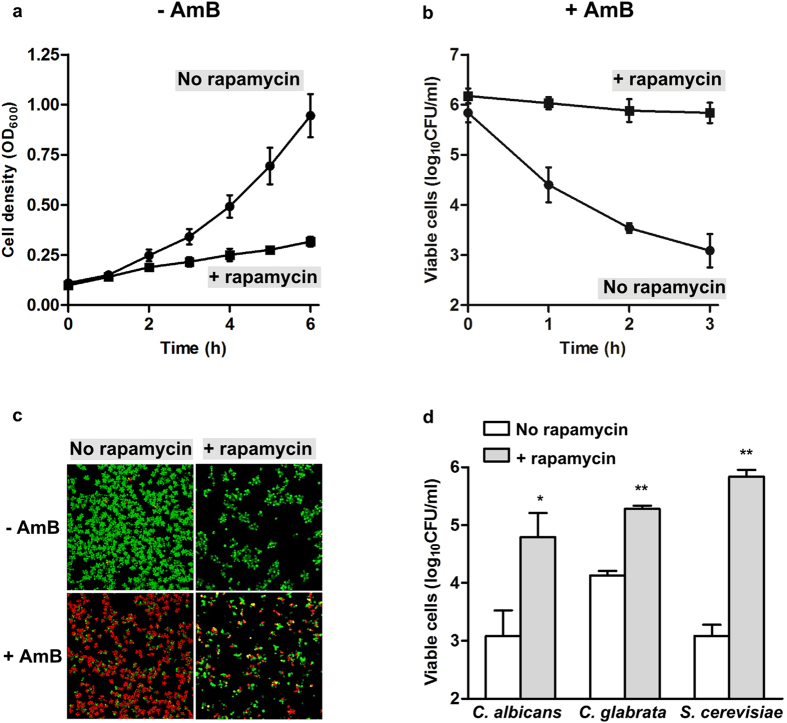
Figure 4. TORC1 inhibition mediates amphotericin B tolerance in wild-type planktonic and biofilm cultures.
(a) Planktonic cells grown in YPD were treated with 1 μg/ml rapamycin (+rapamycin) or untreated (no rapamycin). Samples were extracted hourly for optical density measurements. n = 3, error bars show standard deviation. (b) Survival of exponential growing (No rapamycin) or rapamycin treated (+rapamycin, 1 μg/ml) planktonic cells exposed to 10 μg/ml amphotericin B (AmB). Viability was measured as colony-forming units (CFUs). n = 3, error bars show standard deviation. (c) Confocal laser scanning microscopy of AmB activity against four-hour biofilms after pre-exposure to 1 μg/ml rapamycin or no rapamycin. Survival is visualized with LIVE/DEAD staining. Green, live cells; red, dead cells. (d) Survival of exponential growing (No rapamycin) or rapamycin treated (+rapamycin, 1 μg/ml) planktonic cells exposed to five times MIC amphotericin B (AmB, 5 μg/ml against Candida spp. and 10 μg/ml against S. cerevisiae). Viability was measured as colony-forming units (CFUs) after 3 hours treatment. n = 3, error bars show standard deviation. Statistical significance between rapamycin treated and untreated samples was evaluated with Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001.