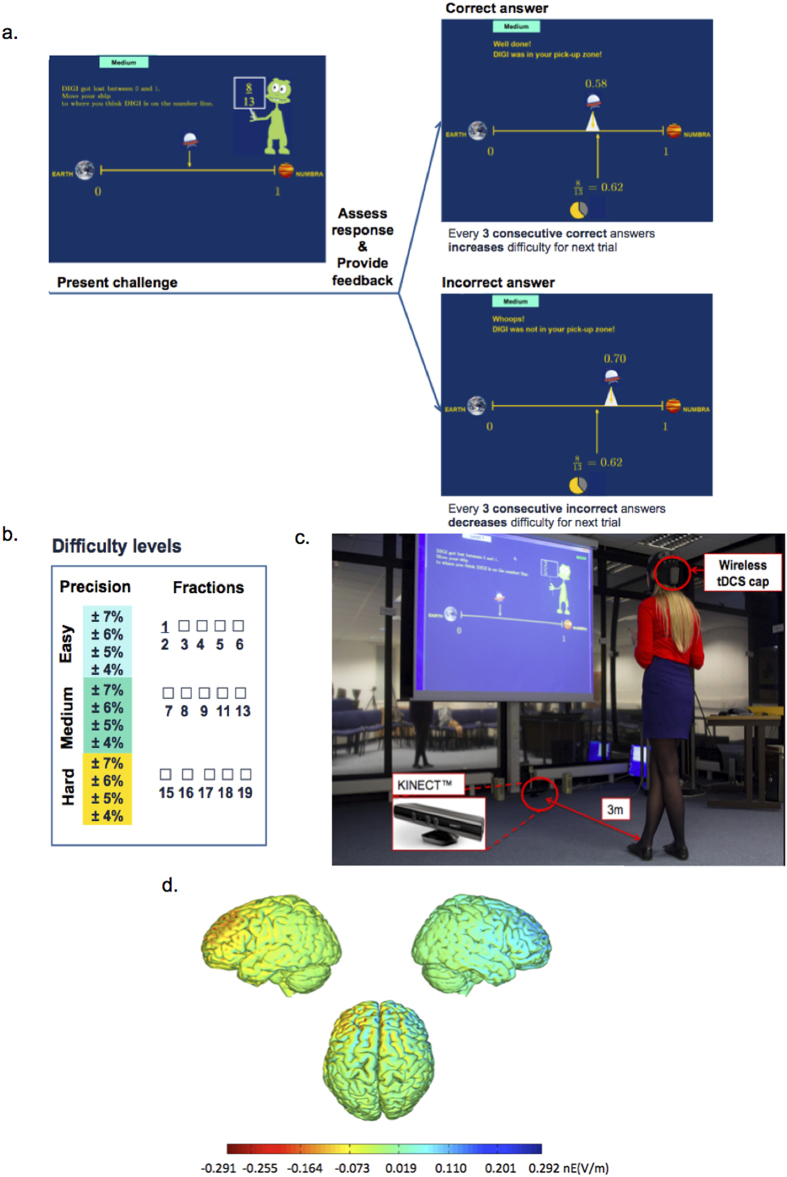
Figure 1.
Coupling brain stimulation with a video game to enhance learning: (a) Sequence of a trial, adaptive game design. Feedback includes both concrete and abstract numerical representations to strengthen fractions understanding57 (For a magnified view, please see Supplementary Figure S3). (b) Types of fractions attempted. Depending on participants’ performance, the difficulty was systematically adjusted as a function of fraction category (Easy, Medium, Hard), and precision (accepted deviations from the correct target; ±7%, ±6%, ±5%, ±4% of the number line range). This is to challenge participants to map fractions with greater accuracy, at their maximal capacity. (c) Experimental setup included a video game that requires body movements, detected by a motion detector coupled with wireless tDCS. Participants move their bodies side-to-side to locate a spaceship on a virtual number line according to fractions presented on a 1.5 × 1.2 meters screen, 3 meters away from their standing position. (d) Computational simulation of current field intensity map over the right-anodal (blue) and left-cathodal (red) dlPFC produced by Neuroelectrics using the modeling engine of the NIC software. Applied currents are maximally concentrated on the cortical surface directly underneath the stimulating electrodes58,59,60.