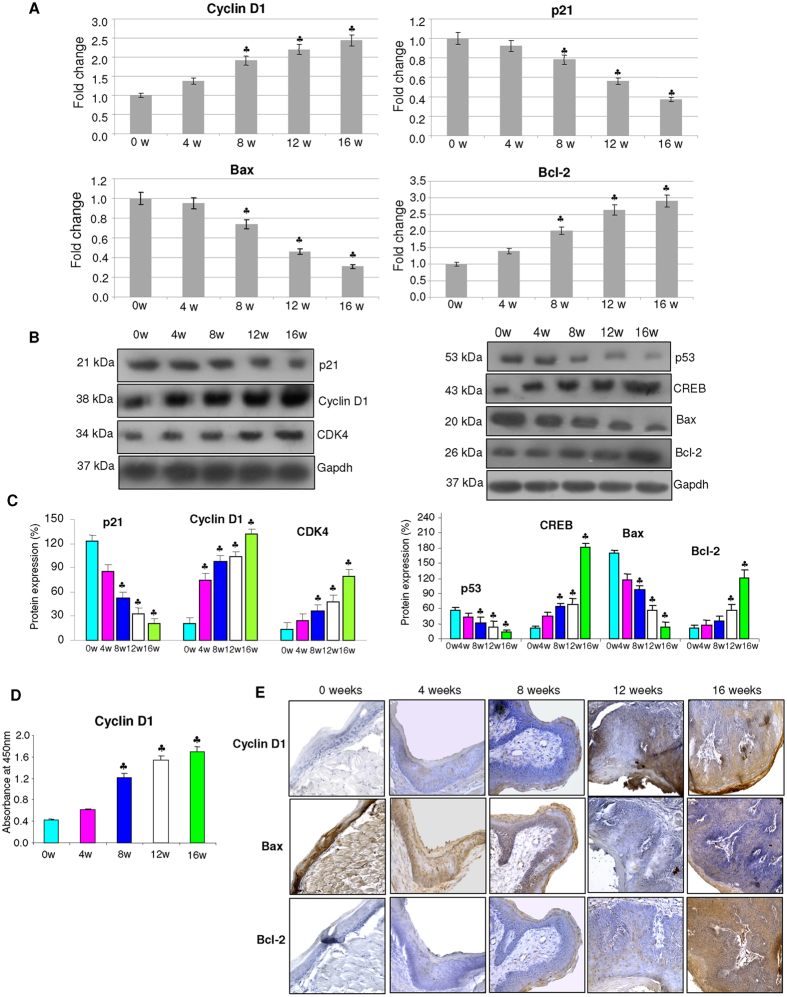
Figure 3. The expression of key molecules involved in cell cycle and apoptosis during the sequential progression of HBP carcinomas (mean ± SD; n = 3).
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Cyclin D1, p21, Bax and Bcl-2 in the buccal pouch tissues of control and DMBA painted hamsters determined by kinetic PCR. The fold change in transcript expression for each gene was determined using the 2−ΔΔCt method. Data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by the Mann–Whitney test (p < 0.05). (B) Western blots showing progressive increase in the expression of cyclins, anti-apoptotic proteins and decreased expression of p21 and pro-apoptotic proteins in DMBA painted hamsters from 0w to 16w. (C) Densitometric analysis representing expression of key proteins involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis for three independent experiments. (D) Levels of total cyclin D1 quantitated by ELISA showing a progressive increase from 0 to 16 weeks of DMBA painting.(E) Representative photomicrographs of immunohistochemical staining of Cyclin D1, Bax and Bcl-2 in control and DMBA painted animals (×40). ♣p < 0.05 versus control.