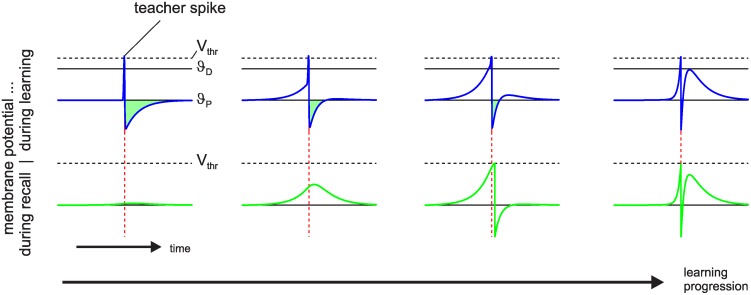
Fig 3. Hebbian learning with homeostatic MPDP.
A postsynaptic neuron is presented the same input pattern multiple times, alternating between teaching trials with teacher spike (blue trace) and recall trials (green trace) to test the output. Initially, all weights are zero (left). The green area between the voltage and threshold for potentiation ϑP signifies the total amount of potentiation, similarly the red area between voltage and ϑD for depression; the latter is only visible in the second to right panel. Learning is Hebbian initially until strong depolarization occurs (second to left). When the spike first appears during recall, it is still not at the exact location of the teacher spike (second to right). Continued learning moves it closer to the desired location. Also, the time windows of the voltage being above ϑD and below ϑP shrink and move closer in time (right). Synaptic plasticity almost stops. The number of learning trials before each state is 1, 16, 53, and 1600 from left to right.