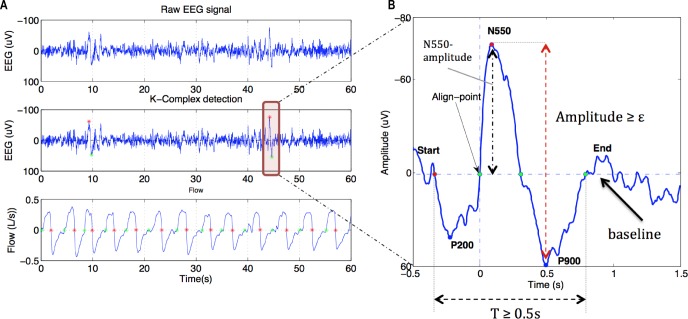
Figure 2.
Detection of K-complexes and their properties. (A) K-complexes were detected according to a peak-to-peak amplitude threshold (ε) as shown by the red and green stars on the electroencephalography (EEG) channel. Green stars on the flow signal reflect the automatic detection of the onset of inspiration and red stars reflect the start of expiration. (B) K-complex component detection. Baseline was calculated as the mean of EEG amplitude during the 1-min window on continuous positive airway pressure (horizontal dashed line). The point at which K-complexes were aligned for ensemble averaging is highlighted (align point) as are the start (red dot) and end points (last green dot). P200 is the minima of the EEG waveform between the start point and the align point. N550 and P900 are maxima (black vertical dashed arrow) and minima of the detected K-complex. Only K-complexes that lasted ≥ 0.5 s *(T) and where the peak-to-peak amplitude was ≥ ε (red vertical dashed arrow) were selected for analysis. ε was set to 50, 75, and 100 μV, respectively.