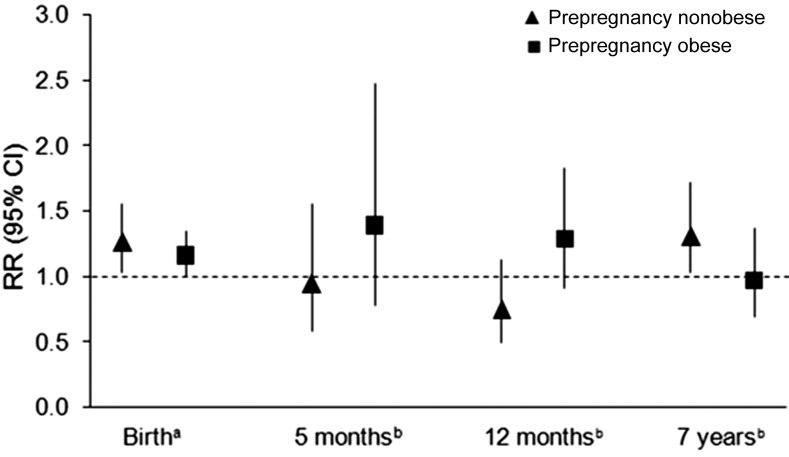
FIGURE 1.
RR and 95% CI for the association between each 1-mmol/L increase in fasting plasma glucose concentrations during pregnancy and offspring risk of macrosomia at birth and overweight/obesity at age 5 mo, 12 mo, and 7 y by prepregnancy obesity status [nonobese: BMI (in kg/m2) <30; obese: ≥30]. The numbers of children born to women who were nonobese/obese before pregnancy were 382/237, 241/142, 231/145, and 210/117 at birth and the 5-mo, 12-mo, and 7-y follow-up, respectively. aRR (95% CI) for macrosomia at birth was calculated by using Poisson regression with robust SEs, adjusted for maternal age at index child's birth, parity, socioeconomic status, prepregnancy BMI, smoking during pregnancy, gestational age at oral-glucose-tolerance test, gestational weight gain, and gestational age at delivery. bRR (95% CI) for overweight/obesity at each follow-up was calculated by using Poisson regression with robust SEs, also adjusted for birth weight besides covariates for macrosomia. P-interaction for fasting plasma glucose concentrations by prepregnancy obesity = 0.61, 0.50, 0.57, and 0.07 for macrosomia at birth and overweight/obesity at age 5 mo, 12 mo, and 7 y, respectively.