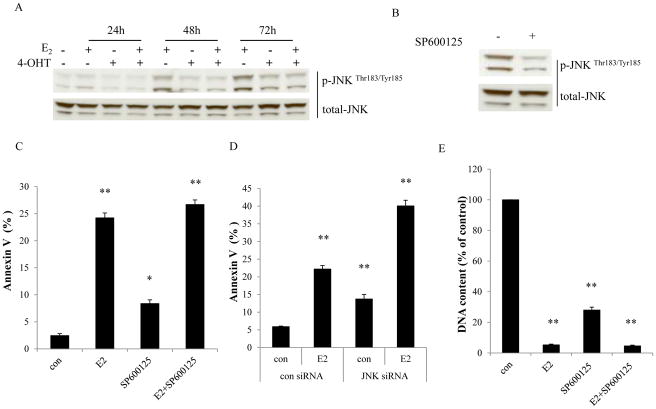
Figure 2. Activation of JNK by E2 in MCF-7:5C cells.
(A) Activation of JNK by E2. MCF-7:5C cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% EtOH), E2 (10−9 mol/L), 4-OHT (10−6 mol/L), and E2 (10−9 mol/L) plus 4-OHT (10−6 mol/L) for the time points indicated. p-JNK was examined by Western blotting. Total JNK was measured as loading control. (B) The JNK inhibitor effectively blocked phosphorylation of JNK. MCF-7:5C cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or SP600125 (10−5 mol/L) for 24 hours. p-JNK was examined by Western blotting. Total JNK was measured as loading control. (C) The JNK inhibitor could not block E2-induced apoptosis. MCF-7:5C cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO), E2 (10−9 mol/L), SP600125 (10−5 mol/L), and E2 (10−9 mol/L) plus SP600125 (10−5 mol/L) for 72 hours. Annexin V binding assay was used to detect apoptosis. p<0.05, * compared with control. p<0.001, ** compared with control. (D) Knockdown of JNK could not block E2-induced apoptosis. MCF-7:5C cells were transfected with control siRNA or JNK siRNA for 72 hours. Then, cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% EtOH) or E2 (10−9 mol/L) for 72 hours. Annexin V binding assay was used to detect apoptosis. p<0.001, ** compared with control. (E) Growth response to the JNK inhibitor in the presence or absence of E2. MCF-7:5C cells were treated with the same compound as in (C). Cells were harvested after 7 days treatment and cell viability was quantitated by determination of total DNA. p<0.001, ** compared with control.