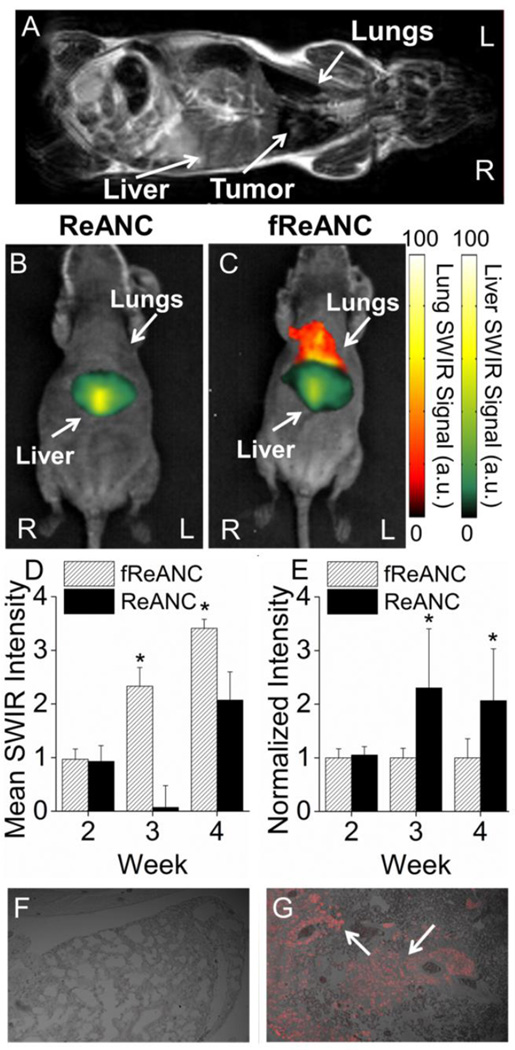
Figure 6. Targeted fReANCs allow for detection of microscale lung lesions.
Nude mice were inoculated i.v. with CXCR4 expressing MBA-MB-231 cells. Cells colonized in the lungs and were monitored using MRI (A). Xenograft mice were administered either ReANCs (B) or fReANCs (C) at early stages (< 6 weeks) after inoculation. SWIR signal from the lung region was quantified at 24 h (D) post-injection. The fReANC associated SWIR signal was greater than the ReANC signal for early time-points, correlating to the presence of microlesions quantified by volumetric reconstruction of the MRIs. The SWIR signal from the liver was quantified for 0 h post injection (E) and showed a 2 fold increase in ReANC accumulation in the organs of clearance. Representative images (n=6) shown in all instances from week 3 of the study. The presence of tumors in the lungs was confirmed with vimentin staining of healthy (F) and tumor bearing (G) lungs, with the red fluorescence marked by arrows indicating tumor cells. (D) Error bars indicate SEM for n = 6. * indicates p < .01 (Wilcoxson Rank-Sum test) (E) * = p < .05 (Wilcoxson Rank-Sum test)