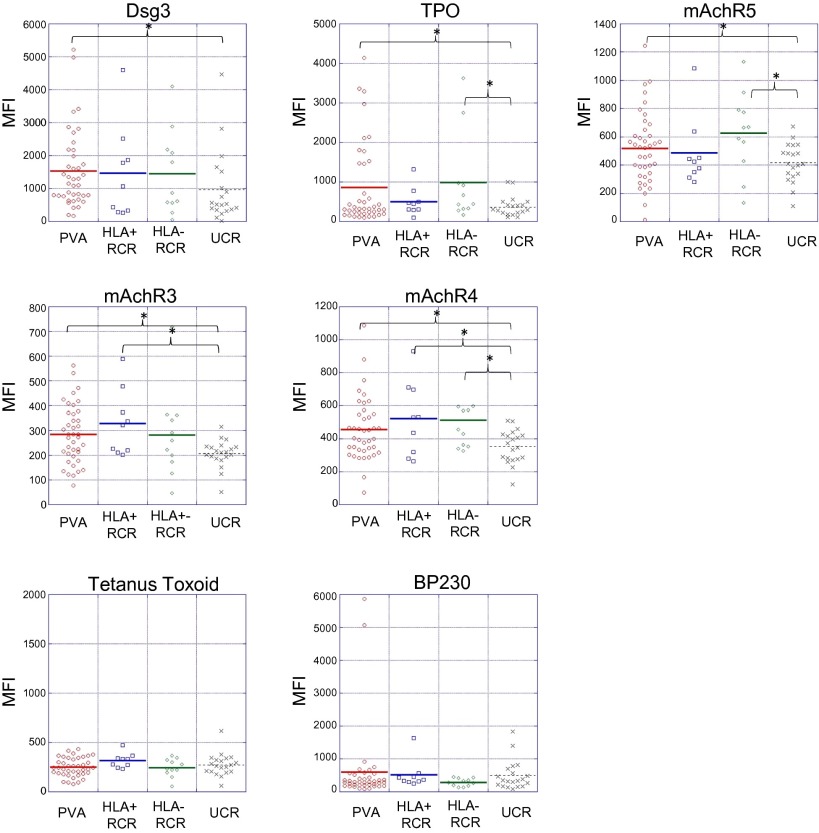
Fig. 4.
Related control subjects exhibit increased levels of reactivity toward the same antigens recognized by patients with active PV. Microarray analysis of autoAb reactivity in related control subjects reveals an increase in autoAb reactivity toward a subset of the antigens recognized by patients with active PV. Presence or absence of a disease-associated HLA allele in related control subjects underlies unique autoAb reactivities (asterisk indicates differences in array reactivity determined to be significant by SAM; q < 0.05). No significant differences in reactivity toward Ttox or BP230 were observed between the groups. Units shown reflect mean fluorescence of antigen triplicates normalized to the appropriate negative control. HLA+ indicates expression of the PV-associated HLA alleles DRB1*0402 and/or DQB1*0503, HLA− indicates the absence of either allele. PVA, active PV; UCR, unrelated control subjects; RCR, related control subjects.