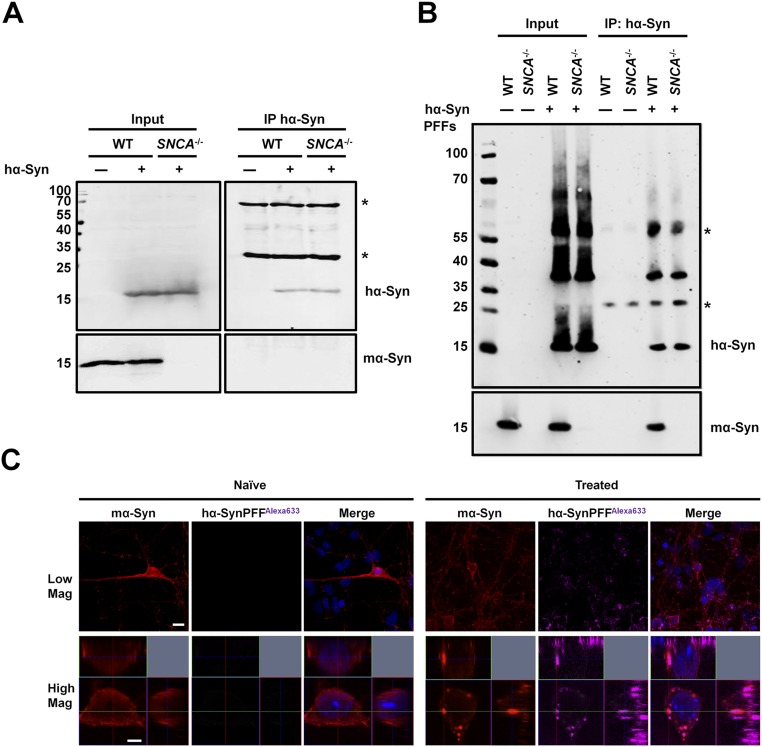
Fig. S7.
Endogenous mα-Syn interacts with fibrillar rather than monomeric hα-Syn species in WT primary neurons. (A) WT or SNCA−/− primary neurons expressing hα-Syn were lysed, and hα-Syn was immunoprecipitated. Although hα-Syn was pulled down successfully, no mα-Syn was detected, thus ruling out the presence of a strong interaction between the two proteins in primary neurons. Western blotting of input solutions established similar protein levels before immunoprecipitation. (B) WT primary neurons treated with 0.1 µM sonicated hα-Syn PFFs for 3 d were lysed, and hα-Syn was immunoprecipitated. Endogenous mα-Syn was detected in the immunoprecipitated sample comprising hα-Syn PFFs. PFF-treated SNCA−/− primary neurons and naive WT and SNCA−/− neurons were used as controls. Western blotting of input solutions established similar protein levels before immunoprecipitation. The asterisks in A and B indicate the heavy and light chains of the antibody used for immunoprecipitation. (C) Immunolabeling of WT primary neurons treated with 0.1 µM sonicated hα-SynAlexa-633 PFFs for 24 h shows that internalized PFFs colocalize with endogenous mα-Syn. Orthogonal projections of Z stacks verify the intracellular nature of inclusions, and WT neurons treated with PBS (naive neurons) were used as controls. (Scale bars: 10 µm and 2 µm for low- and high-magnification images, respectively.)