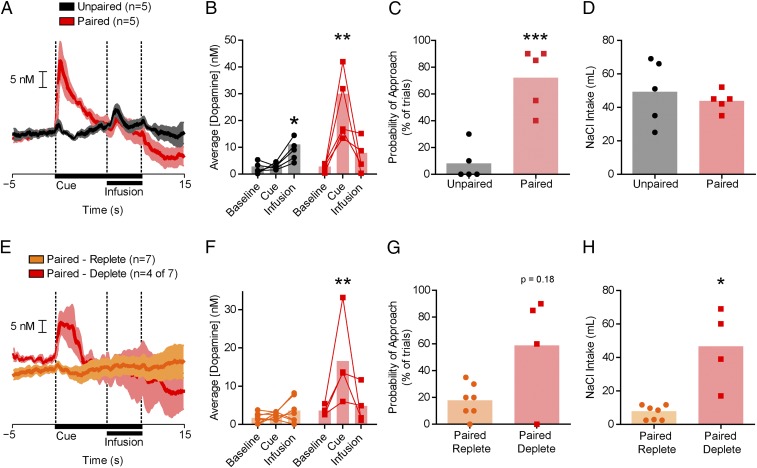
Fig. 4.
CS-US associations are acquired and expressed in a state-dependent manner. (A) Average dopamine concentration (±SEM) for a subset of Paired (n = 5 of 12, red) and Unpaired (n = 5, black) rats. (B) Sodium CS evoked phasic dopamine release only in Paired rats. Paired, CS vs. baseline or infusion (**P < 0.01); Unpaired, infusion vs. baseline or CS (*P < 0.05). (C) Conditioned-approach behavior for Paired and Unpaired rats (***P < 0.001). (D) Postrecording session sodium intake did not differ between Paired and Unpaired rats. (E) Average dopamine concentration (±SEM) in Paired rats tested while replete (Paired-Replete; n = 7 of 12, orange) or deplete (Paired-Deplete; second recording obtained in four of seven rats, red). (F) NaCl CS evoked dopamine only in Paired-Deplete rats. Paired-Deplete CS vs. baseline (**P < 0.01); Paired-Replete, no significant differences (all comparisons, P > 0.05). (G) Conditioned-approach behavior for Paired-Replete vs. Paired-Deplete rats (P = 0.18). (H) Postrecording session NaCl intake for Paired-Replete vs. Paired-Deplete rats (*P < 0.05). Opaque bars represent the mean.