Figure 6.
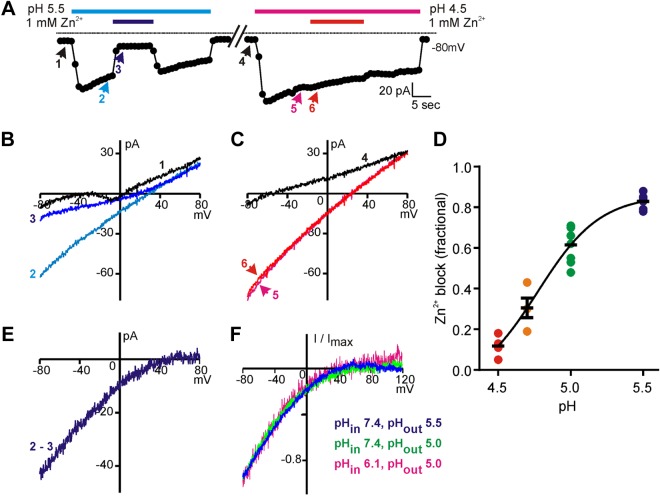
Zn2+ blocks the proton current in a pH-dependent manner. A) Representative example of the block by 1 mM Zn2+ of current evoked in a PKD2L1 taste cell in response to pH 5.5 and pH 4.5 in TEA-MA–based solution. Note that Zn2+ blocks a larger percentage of the acid-evoked current in pH 5.5 than in pH 4.5. B, C) The I-V relationships measured at the indicated time points from the trace in A. D) The fraction of the acid-evoked currents blocked by 1 mM Zn2+ at each indicated pH; data from all cells is plotted, along with the means ± sem. The data were fit with a dose-response curve with a Hill coefficient of 2.0 and IC50 of pH 4.8. E) The I-V relationship of the Zn2+-blocked component of the proton current in B, obtained by subtracting the current recorded in the presence of Zn2+ from the current recorded in its absence. F) The averaged normalized I-V relationships of the Zn2+-sensitive currents recorded at the pHout and pHin indicated (n = 2–7).