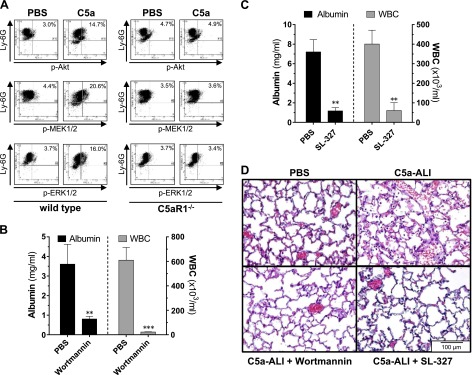
Figure 5.
C5aR1-mediated activation of the PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signaling pathways is essential in the development of C5a-ALI. A) Casein-elicited peritoneal PMNs were isolated from C57BL/6J (wt) mice or C5aR1−/− mice and stimulated with rmC5a (1 μg/ml) or PBS (negative control) for 20 min. Cells were stained for Ly-6G and phospho-Akt(Thr308), phospho-MEK1/2(Ser218/222), or phospho-ERK1(Thr203/Tyr205)/ERK2(Thr183/Tyr185) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. B) Alveolar albumin concentrations and WBC counts 8 h after administration of rmC5a (20 ng/g BW, i.t.) and treatment with the phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor wortmannin (1 µg/g BW, i.p.) or PBS vehicle in C57BL/6J mice. C) Alveolar albumin concentrations and WBC counts 8 h after administration of rmC5a (20 ng/g BW, i.t.) and treatment with the MEK1/2-inhibitor SL-327 (100 µg/g BW, i.p.) or PBS vehicle in C57BL/6J mice. D) Representative lung sections of mice subjected to C5a-ALI (C5a: 20 ng/g BW, i.t. 8 h), treated with wortmannin, SL-327, or vehicle [concentrations as in (B, C)]. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. H&E staining. Magnification, ×400.