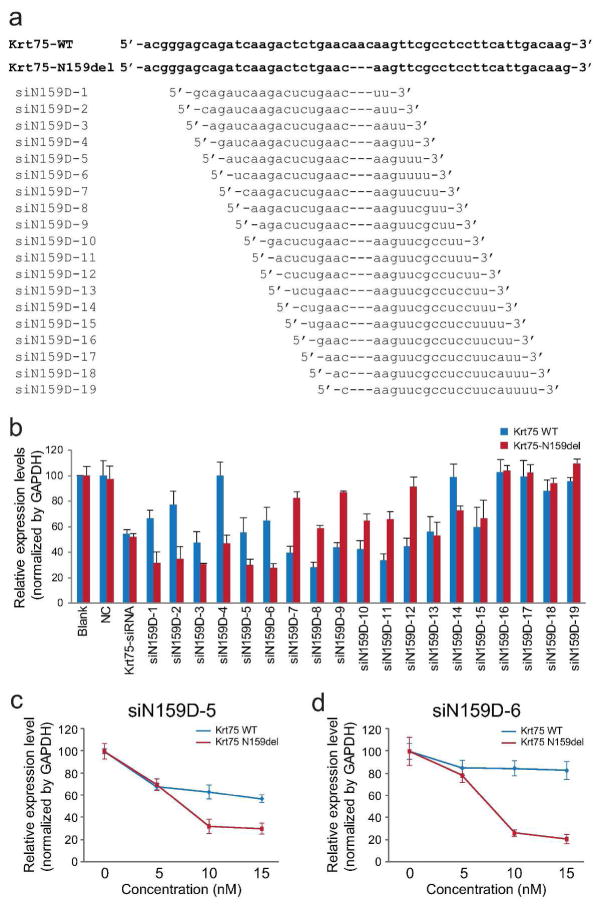
Figure 1. Mutant Krt75-specific siRNA.
(a) Sequences of wild-type and c.545_547del (p.N159del) Krt75 and candidate siRNAs for mutant Krt75. (b) Relative expression levels of wild-type and mutant Krt75 in HEK293T cells co-transfected with wild-type and mutant Krt75 and siRNA (15 nM) by quantitative RT-PCR. Blank, cells transfected with Krt75 expression plasmids without siRNA; NC, cells transfected with negative control (a fragment of inverted beta-galactosidase sequence) siRNA; Krt75-siRNA, a commercially available siRNA against Krt75. (c, d) Relative expression levels of wild-type and mutant Krt75 in cells transfected with 0 − 15 nM siN159D-5 and siN159D-6 siRNAs, as normalized to GAPDH. All experiments were carried out in triplicates in a minimum of three independent experiments.