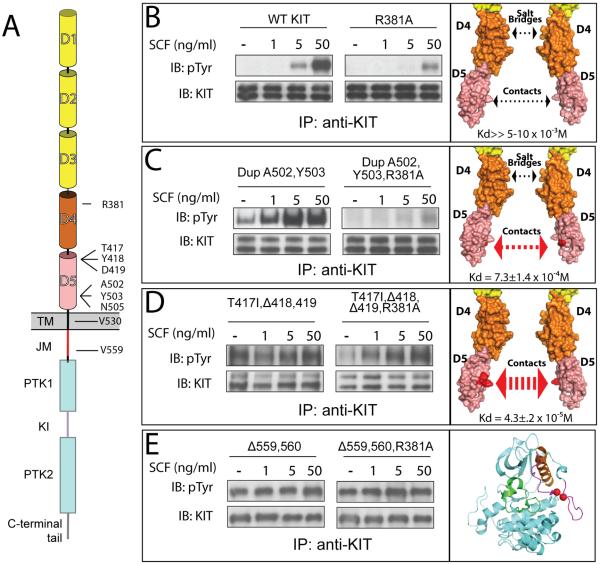
Figure 6. In vivo autophosphorylation of WT or oncogenic KIT mutants.
(A) Schematic representation of full length KIT receptor. D1 – D5 are Ig-like domains. D1–D3 represented with yellow, D4 and D5 with orange and pink cylinders respectively. TM is transmembrane (black), JM - juxtamembrane (red), PTK - protein tyrosine kinase (blue), KI - kinase insert (purple) domains. Oncogenic mutations and Arg381 are labeled.
Tyrosine kinase activity was compared for WT – wild type KIT receptor (B); DupA502,Y503 – duplication of Ala 502 and Tyr 503 (C); T417I ΔY418D419 – substitution of Thr 417 to Ile and deletion of Tyr 418 and Asp 419 (D), and Δ559,560 – deletion of Val 559 and 560 (E). WT or oncogenic KIT mutants (left panel) were compared to those harboring an additional mutation of an Arg 381 (middle panel) - residue responsible for D4:D4 homotypic contacts. NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing WT KIT or oncogenic mutants were stimulated with increasing concentration of SCF (as indicated in the upper panel) for 6 minutes at 37°C. Lysates of unstimulated or SCF-stimulated cells were subject for immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-KIT antibodies followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting (IB) with anti-pTyr (IB: pTyr) or anti-KIT (IB: KIT) antibodies (as indicated). Right panel – surface representation of membrane proximal Ig-like domains (B–D) or cartoon representation of the kinase domain (E), oncogenic mutations are highlighted with red. The strength of D5:D5 contacts and impact of D4 salt bridge schematically represented with arrows. Dimerization constants for D4D5 fragment are shown in the bottom of the right panel.