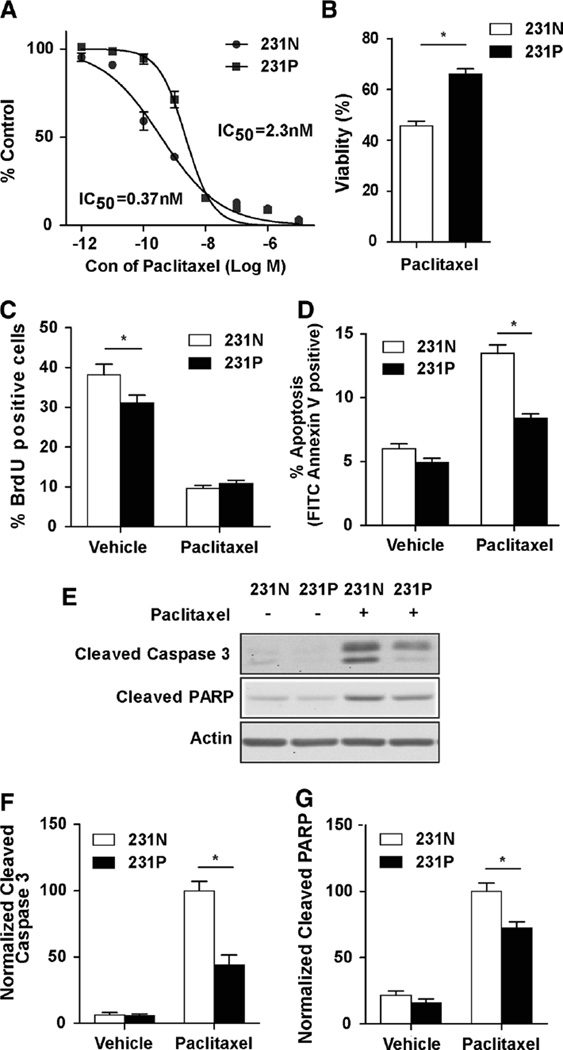
Fig. 1.
Development of paclitaxel-resistant MDA-MB-231 cells with pulse stimulated strategy. a Dose-dependent growth impairment of 231N and 231P cells was identified by sulphorhodamine B assay. The cells were treated in six replicates with pacltaxel for 96 h. b Cell viabilities after 24 h 25 nM paclitaxel treatment compared with vehicle in 231N and 231P cells by trypan blue viability assay (Mean ± SE are shown, n = 3). *p < 0.05. c Cell proliferations after 24 h 25 nM paclitaxel or vehicle treatment in 231N and 231P cells by BrdU incorporation assay (Mean ± SE are shown, n = 3). *p < 0.05. d Cell apoptosis after treatment with 25 nM paclitaxel for 24 h was compared with vehicle in 231N and 231P cells by Annexin V assay (Mean ± SE are shown, n = 3). *p < 0.05. e–g expression of proapoptotic markers were analyzed after 24 h 25 nM paclitaxel treatment compared with vehicle in 231N and 231P cells by Western blot. Representative results are shown in (e). Intensity of the protein bands were determined from three independent experiments by densitometry. Mean ± SE of the relative protein level (normalized to actin) are shown in (f) and (g). *p < 0.05