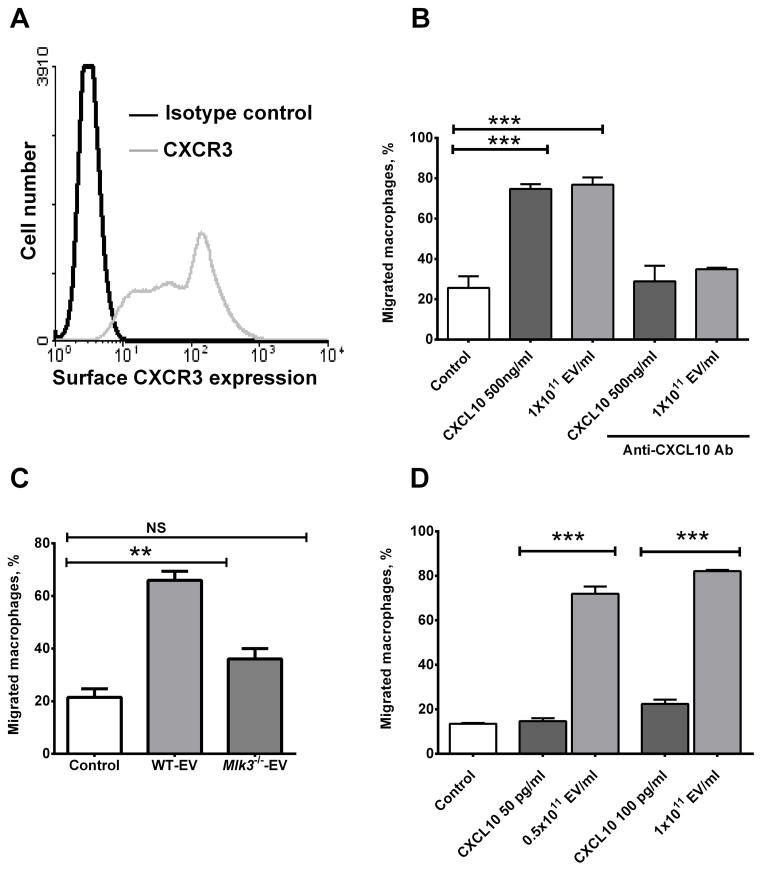
Figure 4. Lipotoxic EVs induce macrophage chemotaxis in a CXCL10-dependent manner.
(A) Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 3 (CXCR3) the (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 (CXCL10) cognate receptor expression was assessed on the bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) cell surface by flow cytometry. (B) Using a modified Boyden chamber, BMDM chemotaxis was assessed by quantification of migrating cells toward either control (media alone), extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) treated wild type (WT) primary mouse hepatocytes (PMH) at a concentration of 1011 particle/ml or CXCL10 recombinant mouse protein at a concentration of 500 ng/ml with or without the CXCL10 neutralizing antibody at 25 μg/ml.(C) BMDM chemotaxis was also assessed by quantification of migrating BMDM toward either EVs derived from LPC-treated WT or Mlk3−/− PMH at a concentration of 1011 EV/ml. (D) 1011 EV/ml contain an equivalent concentration of 100 pg/ml of recombinant mouse CXCL10 (rmCXCL10) as measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The chemotactic potency of 0.5 × 1011 EV/ml and 1 × 1011EVs/ml were compared to an equivalent concentration of rmCXCL10 of 50 pg/ml and 100 pg/ml respectively. Bar columns represent mean ± S.E.M. *** P < .001, ** P < .01 compared to vehicle treatment.