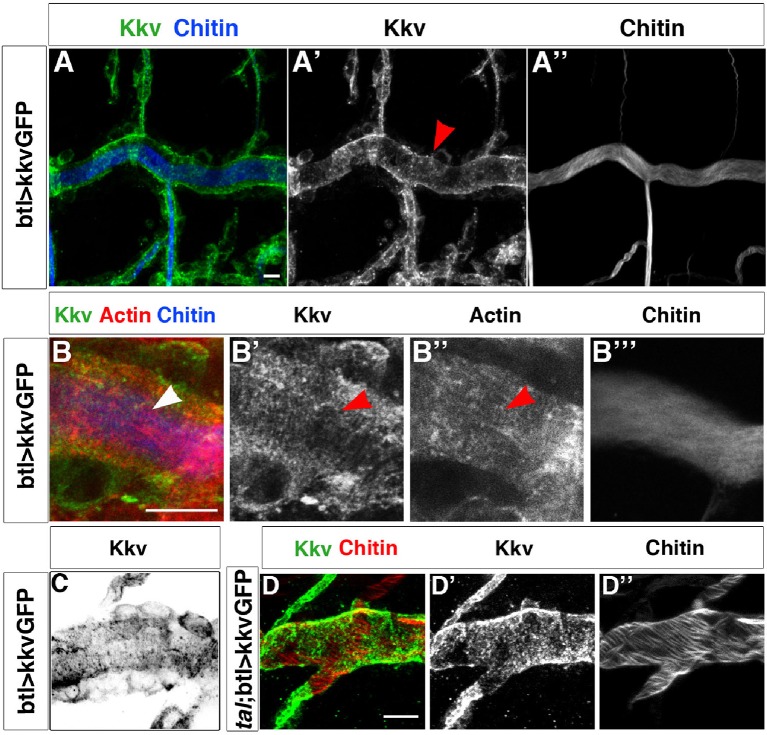
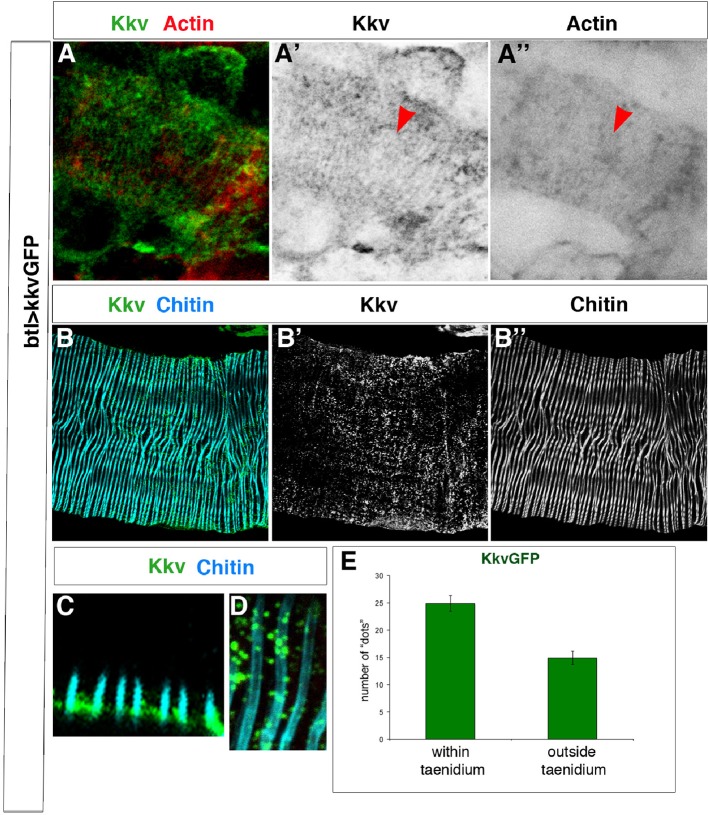
Figure 3. Kkv co-localises with F-actin rings during tracheal maturation.
(A) Detail of stage 16 wild-type embryos expressing a kkvGFP transgene in tracheal cells and stained with fluostain to reveal the chitin filament; Kkv is detected in rings that resemble the F-actin rings (arrowhead in A’). (B) DT zoomed detail of stage 16 wild-type embryos expressing a kkvGFP transgene in tracheal cells and stained with fluostain and phalloidin to reveal the chitin filament and the F-actin rings (arrowheads). (C) Detail of a stage 17 embryo expressing kkvGFP in tracheal cells, showing the localisation of Kkv in rings throughout the length of the tube. (D) Detail of stage 17 tal/pri embryos expressing a kkvGFP transgene and stained with fluostain to reveal the chitin aECM; in tal/pri mutants, Kkv is detected in a punctate pattern throughout stages 16–17 and not in lines or bundles, in contrast to wild-type embryos. In all panels anterior is to the left and scale bars = 10 μm.