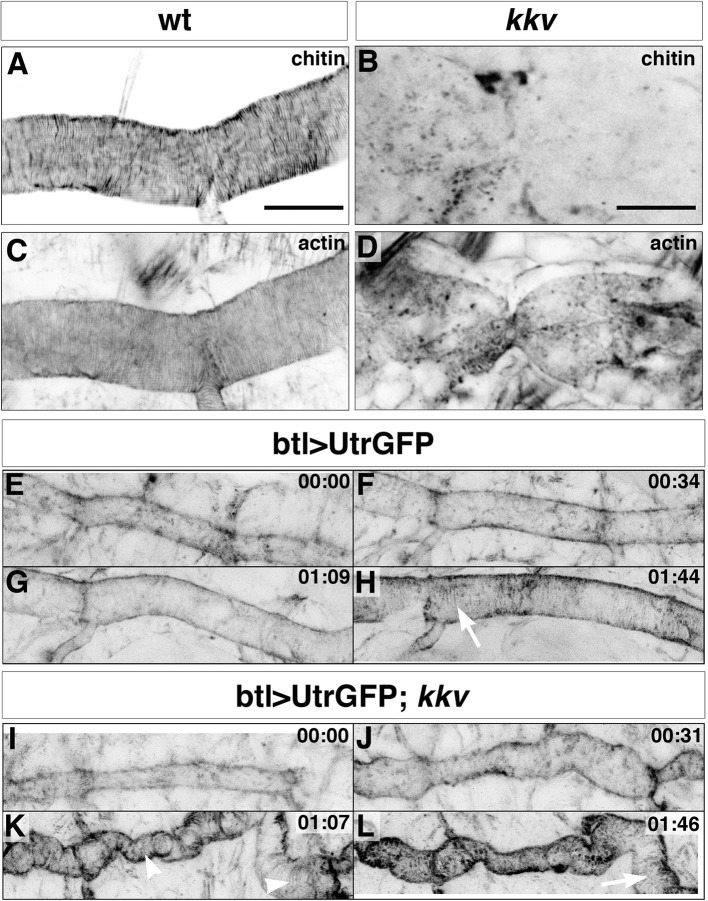
Figure 6. Taenidial folds and F-actin bundles in kkv mutant embryos.
(A-D) Wild-type (A, C) and kkv mutant (B, D) mutant embryos stained with fluostain to label taenidial folds (A, B) and phalloidin to label F-actin bundles (C, D). The taenidial folds and F-actin bundles run perpendicular to the tube axis in the wild-type embryo (A, C) while in kkv mutant embryos taenidial folds are absent and F-actin bundles fail to form (B-D). The images are single stacks of confocal sections. Scale bars = 10 μm. (E-L) Time-lapse images of wild-type (E-H) and kkv mutant (I-L) embryos carrying btlGAL4UASUtrGFP to visualise actin in live embryos. In the wild-type embryo, F-actin bundles (arrow) become visible at the end of time-lapse imaging (H) while in the kkv mutant F-actin bundles form transiently (K, arrowhead) and then disappear (L, arrow).