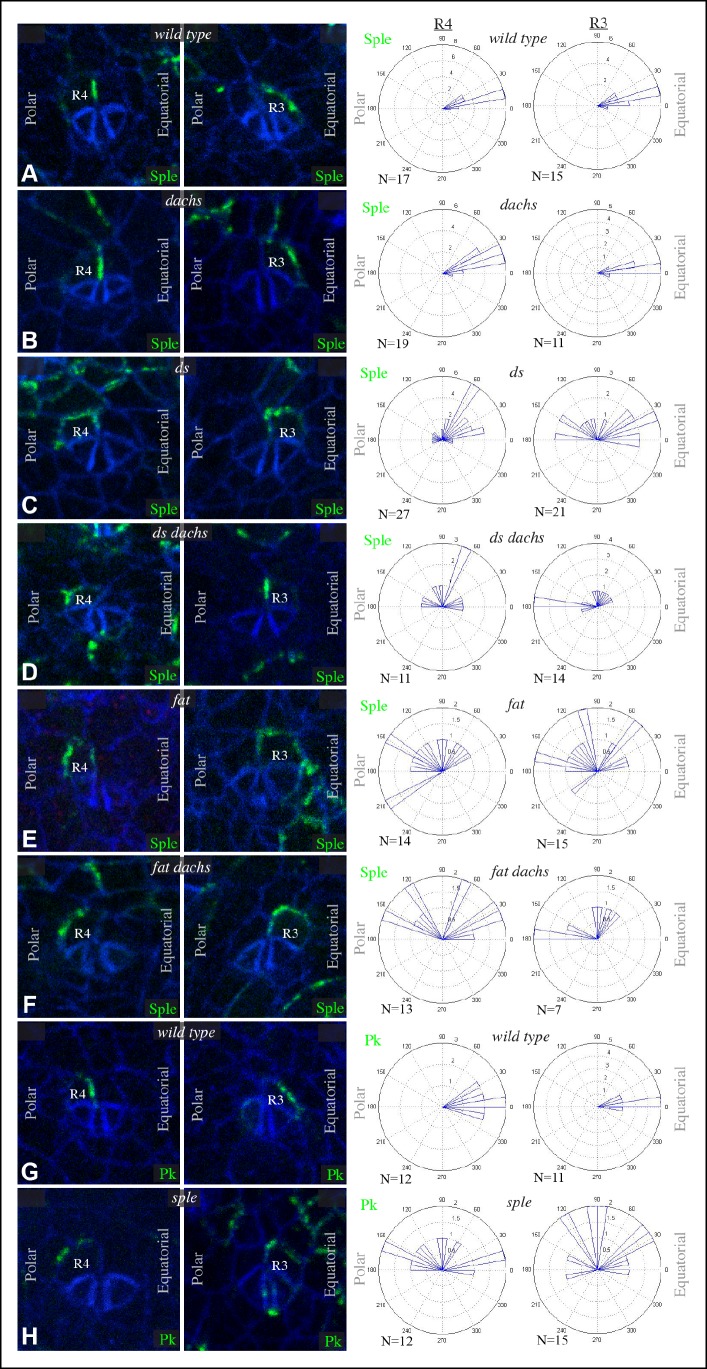
Figure 5. Sple and Pk localization in photoreceptor cells.
Localization of GFP:Sple (A–F) or GFP:Pk (G,H) in cells with expression in R4 or R3 photoreceptor cells in wild type (A,G), dGC13/ d210 (B), ds36D/ dsUA071 (C), dGC13 ds36D/ dGC13 dsUA071 (D), ft8/ ftG-rv (E), dGC13 ft8/ dGC13 ftG-rv (F), and sple1 (H) mutants. Rose plots summarize localization based on the indicated number (N) of examples, with equatorial to the right, polar to the left, and anterior (towards the morphogenetic furrow) at top.