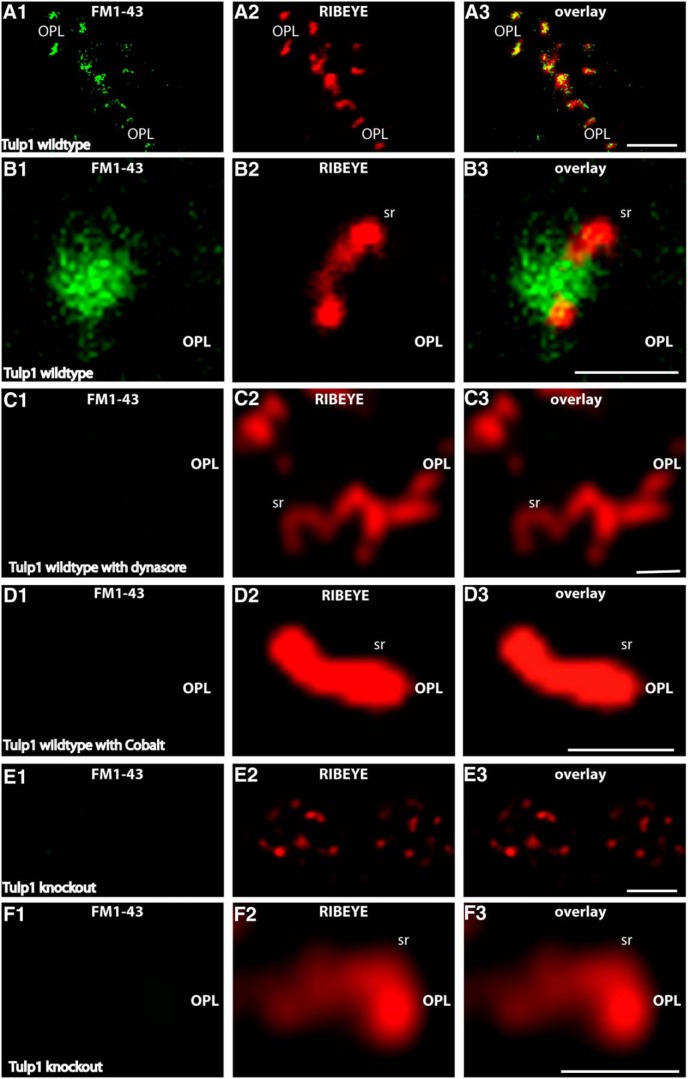
Figure 7.
Retinal slices from P16-d-old control and Tulp1 knock-out mice (from the same litter) were incubated with FM1-43 as endocytic tracer. A, E, Low-magnification survey images of the OPL that contains the photoreceptor synapses in control animals (A) and knock-out animals (E). B–D, F, Higher magnifications of single synaptic ribbon complexes. In the control mice, there was an intense uptake of FM1-43, particularly in close vicinity to the synaptic ribbon (A, B), similar to that previously described (Wahl et al., 2013). The uptake of FM1-43 at the ribbon complex in control mice is dependent on the activity of dynamin. Blocking dynamin activity with dynasore completely abolishes uptake of FM1-43 at the synaptic ribbon in control mice (C), indicating that the FM1-43 signal at the ribbon reflects endocytic uptake. The FM1-43 uptake is also dependent upon vesicle cycling as shown by incubation with cobalt ions (Co2+), which block Ca2+ entry through Cav channels (D). In contrast to the littermate control mice, no uptake of FM1-43 was observed in Tulp1 knock-out mice next to the synaptic ribbon (E, F). Images were obtained by confocal imaging. Results were obtained from 20 slices from Tulp1 knock-out mice and littermate control mice (three mice for each genotype) and collected under identical conditions for both genotypes. sr, Synaptic ribbon; OPL, outer plexiform layer. Scale bars: A, E, 5 μm; B–D, F, 1 μm.