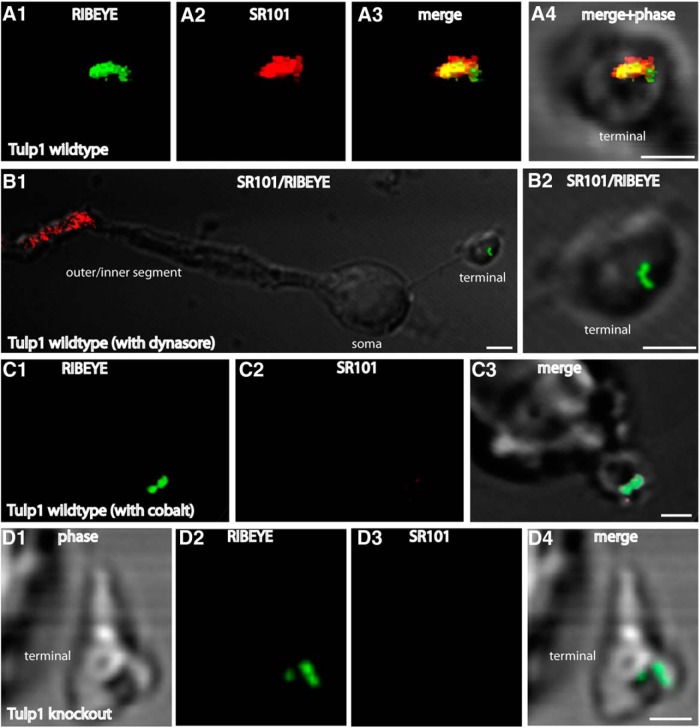
Figure 8.
Photoreceptors were isolated from P16-d-old control and Tulp1 knock-out mice (from the same litter) and incubated with SR101 as extracellular uptake marker. A, As previously described (Wahl et al., 2013), there was an intense uptake of SR101 (A2) in the synaptic terminals of wild-type mice in close vicinity to the synaptic ribbon (A1). The synaptic ribbon was labeled with anti-RIBEYE antibodies (A1). A, Volume view of an immunolabeled terminal obtained from confocal stacks. This uptake of SR101 was dependent upon dynamin because inhibiting dynamin activity with dynasore resulted in a complete inhibition of SR101 uptake in the presynaptic terminal (B). Also, inhibitors of vesicle cycling (e.g., incubation with Co2+), which blocks Ca2+ entry through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, completely inhibited uptake of SR101 in synaptic terminals of wild-type mice (C). Uptake of SR101 was nearly completely abolished in photoreceptor terminals of untreated Tulp1 knock-out mice (D). A–D, Photoreceptor presynaptic terminals can be readily identified by the immunolabeled synaptic ribbon. Isolated photoreceptors were obtained from seven independent experiments (seven mice of each genotype, always littermates). In total, 122 photoreceptors were analyzed from knock-out animals and 109 from control littermates. Images were obtained by confocal imaging and acquired under identical conditions for animals of both genotypes (see also Materials and Methods). Scale bars, A–D, 1 μm.