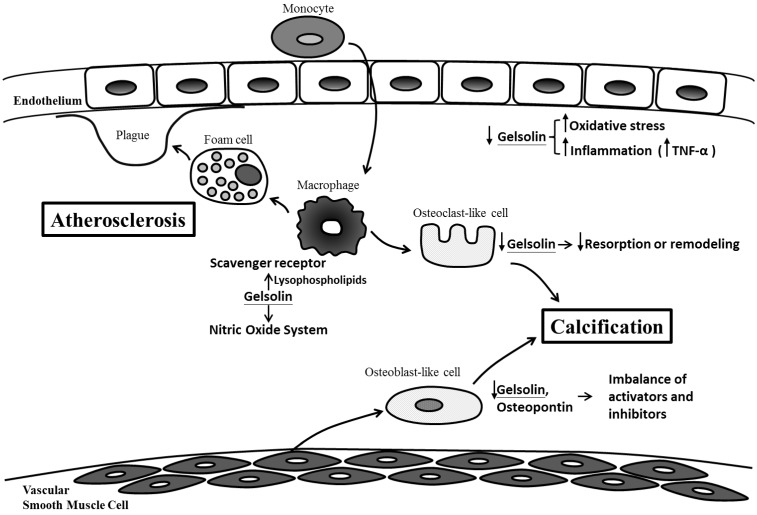
Figure 2.
Possible mechanisms for gelsolin depletion, vascular injury and calcification in chronic kidney disease. Gelsolin depletion may impair modulation on lysophospholipids, macrophage receptor and nitric oxide system which are involved in the maintenance of vascular integrity, development of foam cells, plaque and atherosclerosis. Blood levels of gelsolin have also been correlated inversely with oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines (i.e. TNF-α). In addition to an impaired resorption of calcification by osteoclast-like cells, gelsolin depletion may also exacerbate the imbalance between calcification inhibitors and activators.