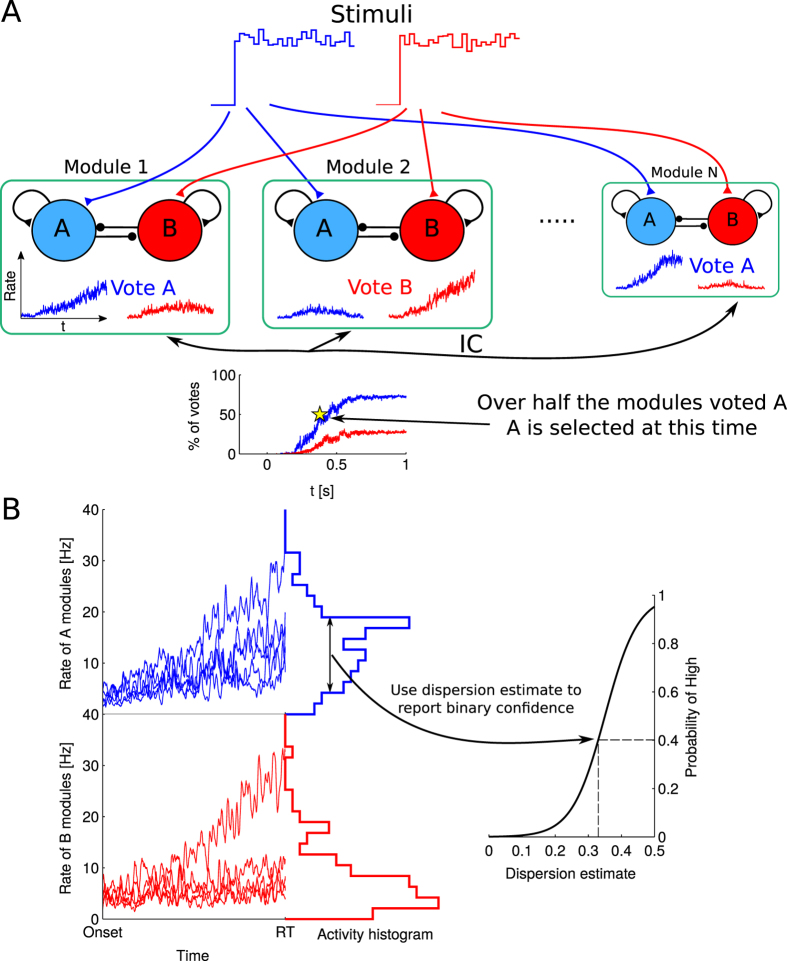
Figure 1. A schematic representation of the model.
(A) shows the decision mechanism. Sensory input of the competing alternatives is fed into the N separate modules. Each module is constructed by an ANN with two populations that have recurrent excitation and lateral inhibition, and receive the external sensory input from one of the two alternatives, and a baseline of noisy background input from other regions of the brain that are not task specific. All the populations are interconnected across modules. This interconnection is regulated by parameter IC. Each module casts a vote in favor of one option depending on the competition’s outcome. When an option is voted by more than half the modules (represented with a star), it is selected as the response. (B) shows the confidence mechanism. All modules integrate evidence and commit to a global choice at a certain time. At that time, the dispersion amongst the selected options firing rate, σdv is estimated, and its value is transmitted to an external layer. This layer assigns the binary confidence report randomly with a sigmoid probability that depends on the dispersion estimate.