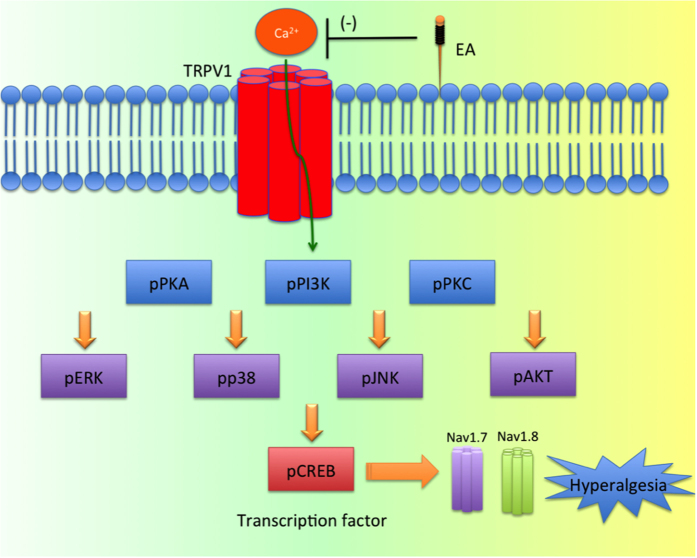
Figure 8. Schematic illustration of possible mechanisms in EA-mediated analgesia of CFA-induced inflammatory pain.
Summary diagram of how TRPV1 is crucial for inflammatory pain and related mechanisms. Our results show that TRPV1 acts as a receptor in inflammatory pain. Activation of TRPV1 increases the expression of pPKA, pPI3K, pPKC. Furthermore, pERK, pp38, pJNK, pAKT, and pCREB were also increased. Moreover, nociceptive Navs were increased for pain conduction. Aforementioned molecules could be attenuated in TRPV1−/− mice.