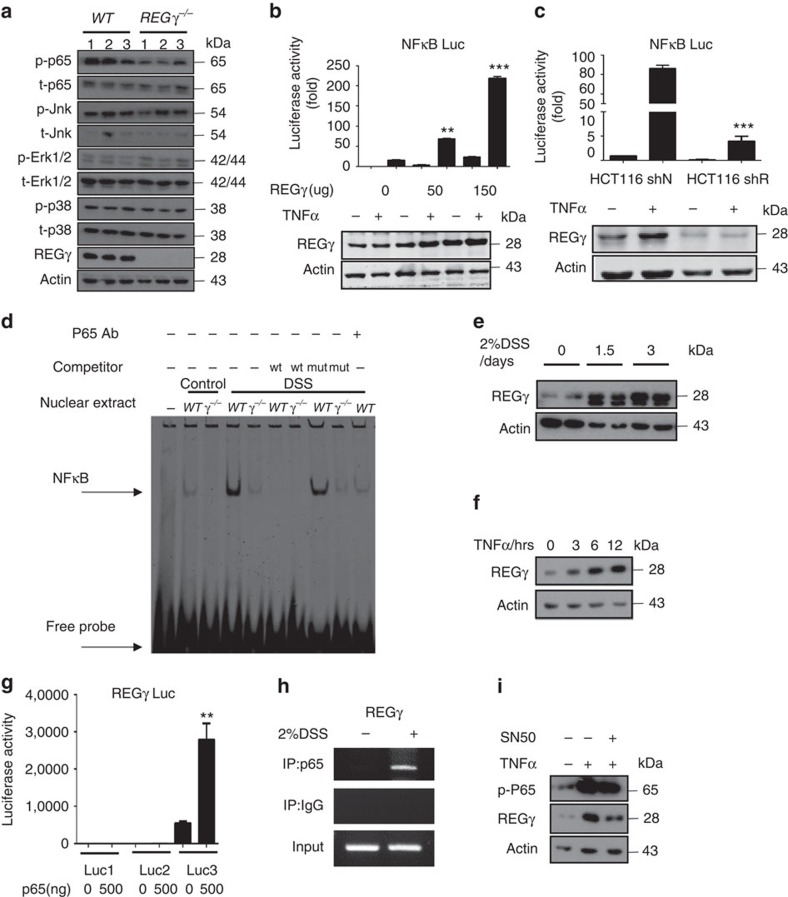
Figure 4. Reciprocal regulation of REGγ and NFκB pathway in colon epithelial cells.
(a) Colon epithelial cells collected from WT or REGγ−/− mice at 7 days after DSS administration were examined for activation of NFκB and MAPKs by western blot analysis. Each lane represents a sample from an individual mouse. (b,c) NFκB luciferase reporter activities were measured upon indicated REGγ overexpression (b) or knockdown (c) in HCT116 cells before and after 6 h TNF stimulation. n=3 per group. Data represent means±s.e.m. from three independent experiments. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001, Student's t-test. (d) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay using nuclear extracts of colon epithelial cells from WT or REGγ−/− mice challenged with 2% DSS for 0 day or 7 days. Oligos containing NFκB consensus binding site were used as a probe. Representative image are from one representative experiment of the two repeats. (e,f) Expression of REGγ was detected in colon epithelial cells isolated from mice after 2% DSS administration for 0, 1.5 and 3 days (e) and in HCT 116 cells after indicated TNFα stimulation (f). Representative images were from one representative experiment of three repeats. (g) REGγ-luciferase reporter containing the cluster-3 NFκB binding elements was responsive to p65-mediated transcriptional regulation. n=3 per group. Data represent means±s.e.m. from three independent experiments. **P< 0.01, Student's t-test. (h) ChIP assays on REGγ promoter were performed in colon epithelial cell of mice after 2% DSS administration for 3 days. Representative of three repeats. (i) NFκB inhibitor, SN50, attenuated TNFα-mediated elevation of REGγ. Representative data were from three repeats.