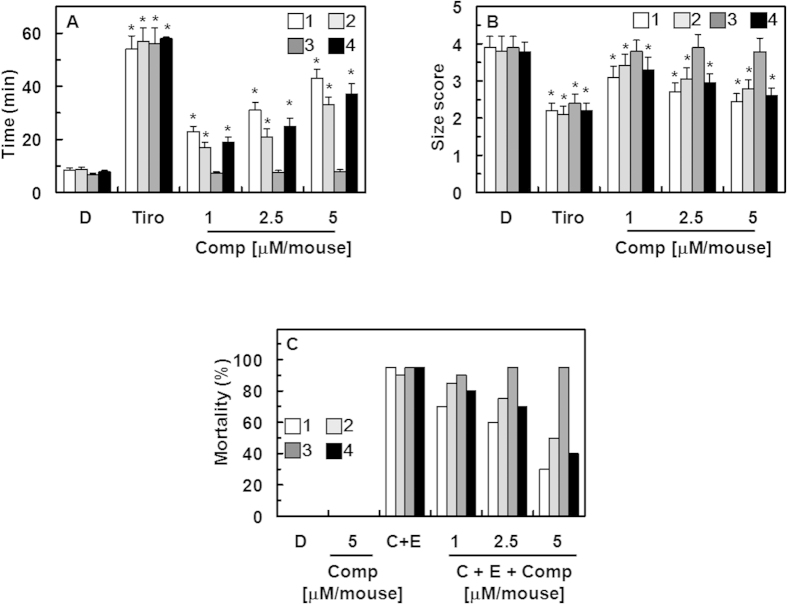
Figure 4. Effects of compounds 1–4 on arterial thrombosis and on acute thrombosis.
(A) Time to large thrombus formation by compound 1 (white box), 2 (light gray box), 3 (dark gray box), and 4 (black box). Tirofiban (Tiro) was used as a positive control. (B) The size score of the thrombus at 60 min after FeCl3-treatment as described in “Materials and Methods”. (C) After each compound was injected intravenously, a mixture of collagen (C, 500 μg/kg) plus epinephrine (E, 50 μg/kg) was injected into the tail vein of mice to induce acute thrombosis 6 h later. Then, mice (20 mice per group) were carefully examined for 15 min to determine whether the mouse was paralyzed, dead, or recovered from the acute thrombotic challenge. D = 0.2% DMSO used as the vehicle control. *p < 0.05 vs. DMSO.