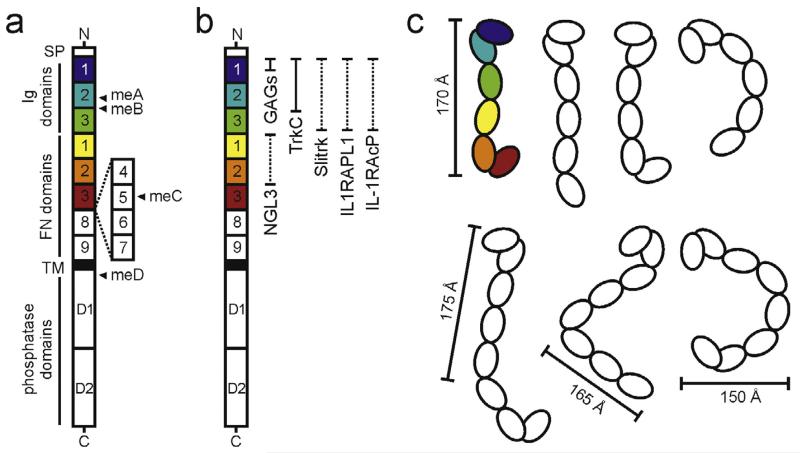
Fig. 2.
Architecture and flexibility of the type IIa RPTP ectodomain. (a) Domain organisation of the type IIa RPTPs. N, amino-terminus (extracellular); SP, secretion signal peptide; TM, transmembrane; C, C-terminus (intracellular); Ig, immunoglobulin-like; FN, fibronectin type-III. Alternative splicing of the type IIa RPTPs by insertion of FN domains 4–7 and mini exons A–D (closed arrowheads) generates many isoforms, which exhibit distinct expression patterns [35,39]. Additional isoforms, lacking Ig3 (RPTPσ) or FN5 (LAR) domains, have also been reported [37,41]. (b) Type IIa RPTP domains required for binding to the listed extracellular ligands are illustrated by filled or dashed vertical bars (structural information currently available or unavailable respectively). (c) Cartoon illustrating the flexibility revealed by combined crystallographic, electron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering analyses of the human RPTPσ ectodomain. Conformations representative of Ig1-FN3 (top) and short ectodomain (bottom) molecules are depicted [57]. The conformation corresponding to the human RPTPσ Ig1-FN3 crystal structure (PDB accession code 4PBX) is coloured. Approximate molecular dimensions are indicated.