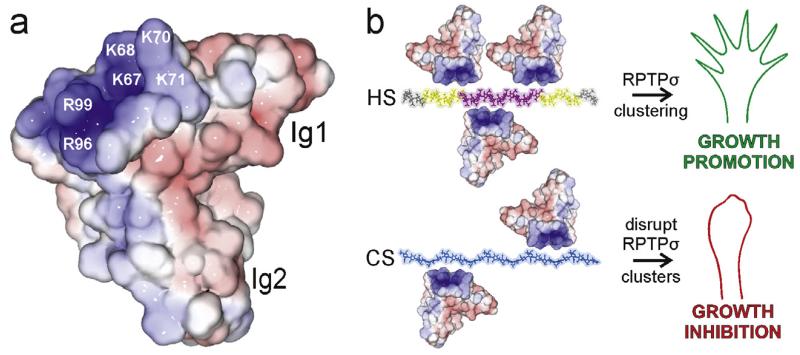
Fig. 3.
Structural and functional consequences of type IIa RPTP-proteoglycan binding. (a) Solvent accessible surface of human RPTPσ Ig1-2 (2YD3 [58]) coloured by electrostatic potential from red (−8 kT/e) to blue (+8 kT/e). Labelled residues are important for proteoglycan binding (numbering corresponds to chicken RPTPσ). (b) Model for HS-induced clustering of the type IIa RPTPs believed to result in neuronal extension (top). Disruption of type IIa RPTP clusters through interaction with CS results in growth inhibition (bottom). The heparin 30-mer is coloured to indicate zones of differing sulphation level in HS: grey (low), intermediate (yellow) and high (pink). GAG chains were built from the following PDB accession numbers: heparin (1HPN [145]) and chondroitin-4 sulphate (1C4S [146]).