Fig. 7.
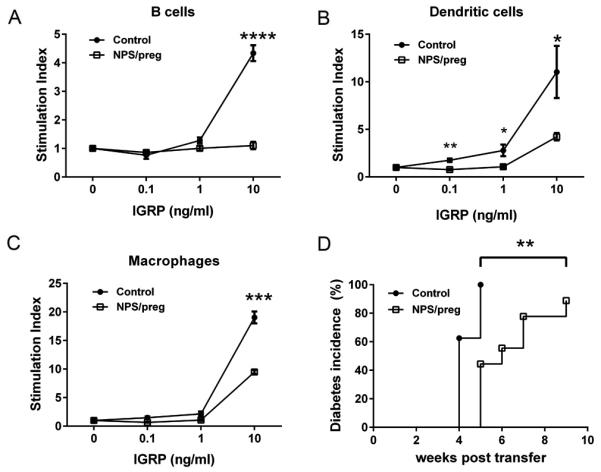
Tolerogenic function of APC in vitro and in vivo. In vitro: splenic B cells (A), dendritic cells (B) and macrophages (C) were purified from control NOD or NPS/preg mice (N=4/group). Irradiated B cells (5×104), dendritic cells (5×103), and macrophages (5×103) were incubated with purified CD8+ T cells (1×105) from NY8.3 NOD mice, together with different concentrations of IGRP206-214 peptide as described in Fig.6. Statistical differences were analyzed by t-test - *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001, ****, p<0.0001. (D) In vivo: Purified total splenic APCs were isolated either from control NOD or NPS/preg mice, and purified total splenic T cells were isolated from diabetic NOD mice. Three million APCs and two million T cells were mixed and transferred to 5-week-old NOD.scid mice (n=9/group). Diabetes development was monitored twice a week by glycosuria and confirmed by blood glucose ≥ 250mg/dl. Statistical differences were analyzed by log-rank test, **: p<0.01.
