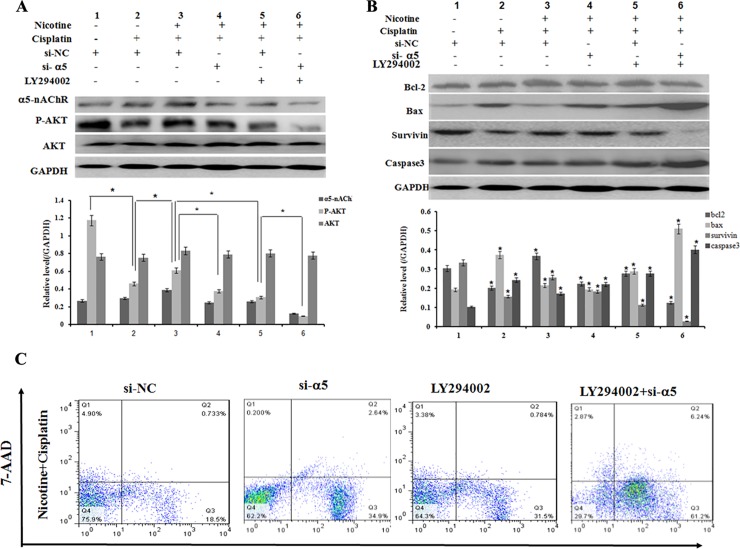
Fig 4. α5-nAChR/AKT signaling involved in anti-apoptotic effects of nicotine in cisplatin-induced apoptosis of BGC823 cells.
A: P-AKT was activated after exposure to 100μM nicotine in BGC823 cells (lane 2 and lane3). Cisplatin strongly suppressed activity of P-AKT (lane 1 and lane 2) but nicotine also induced P-AKT in the presence of cisplatin (lane 2 and lane 3). Down-regulation of α5-nAChR expression decreased the level of P-AKT (lane 4 and lane 5). Treatment with LY294002 downregulated P-AKT expression (lane 3 and lane 5). Combination LY294002 with si-CHRNA5 transfection significantly repressed the nicotine induced P-AKT protein levels (lane 3 and lane 6); *p<0.05; B: Cisplatin induced an increase in caspase-3 and Bax activation in BGC823 cells a decrease in Bcl-2 and Survivin expressions, whereas nicotine blocked cisplatin- induced Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3 and Survivin expressions; With silence of α5-nAChR co-administrated LY294002, an increased apoptosis was observed with the induction of Bcl-2, Bax, Survivin and Caspase-3 by nicotine in BGC823 cells. *p<0.05; C: Assessment of apoptosis by AnnexinV/7-AAD staining in each group. BGC823 cells were pre-treated with 100 μM nicotine and cisplatin for 24 h, and/or si-α5-nAChR for 48h, and/or AKT inhibitor LY294002 for 24h, and harvested.