Figure 4. Hemocytes are required for AiP-induced overgrowth. (See also Figures S3 and S6).
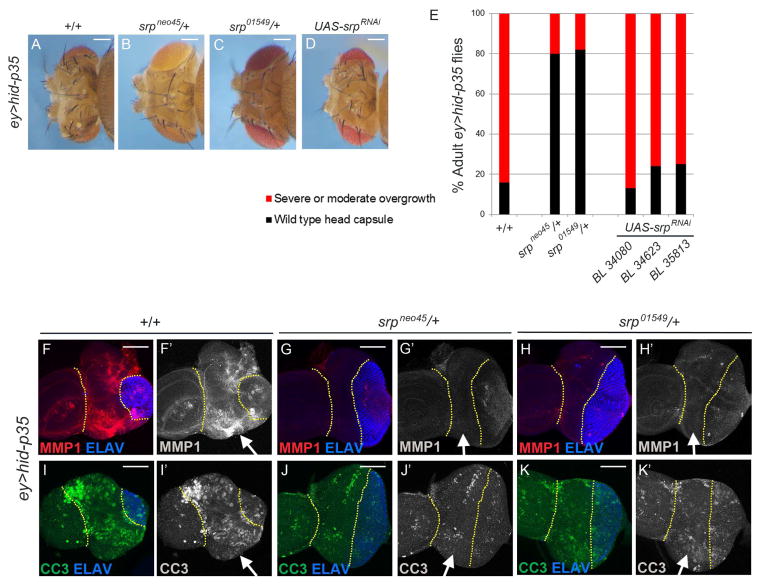
(A–D) Representative examples of adult heads of ey>hid-p35 animals that are either wild-type (A), heterozygous for two serpent (srp) alleles (B,C) or express UAS-srpRNAi transgenes (D). The srp alleles used are indicated above the panels. The srpRNAi line used in (D) is BL34080 from Bloomington Stock center. Similar data were obtained for two additional srpRNAi stocks (see E). Scale bars: 200 μm.
(E) Schematic representation of the effects of srp alleles and srp RNAi on the ey>hid-p35 overgrowth phenotype. Based on qualitative screening criteria (presence of ectopic ocelli and bristles; expansion of mid-head capsule width; see Figure 1B), progeny are scored as wild type (black bars) or having an overgrowth phenotype (red bars). Suppression is determined based on a shift in the percentage to wild-type from overgrown animals that is significantly different based on a Pearson’s chi-squared test for degrees of freedom=1, χ2 = 10.83 at p=.001. See Figure S3G for detailed statistical analysis.
(F,G,H) srp alleles strongly suppress JNK activity in larval eye imaginal discs. Yellow dotted lines mark the undead tissue (arrows). MMP1 labeling (red in F,G,H; grey in F′,G′,H′) was used as a JNK activity marker. ELAV labeling (blue) indicates normalization of eye disc patterning by heterozygous srp alleles. Scale bars 50 μm.
(I,J,K) CC3 is reduced, but not absent, by srp alleles (green in I–K; grey in I′–K′) suggesting that hemocytes participate in the feedback amplification loop in apoptotic cells. As shown in (F–H), the ELAV (blue) pattern is normalized. Yellow dotted lines mark the undead tissue (arrows). Scale bars 50 μm.