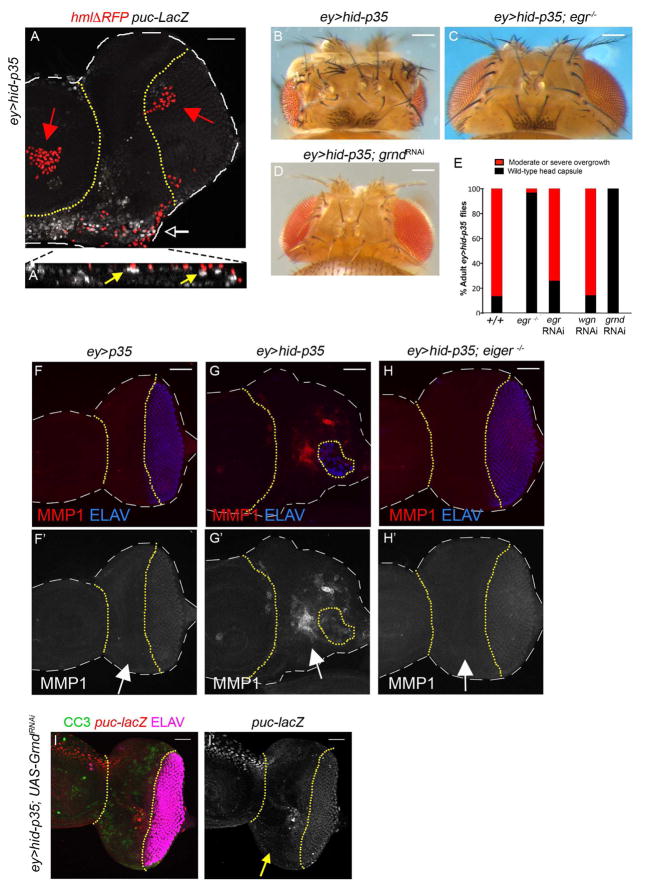
Figure 5. Hemocytes activate JNK through the TNF system Eiger/Grindelwald. (See also Figure S3).
(A) Shown is a mildly overgrown ey>hid-p35 larval eye-antennal imaginal disc. Dashed white lines outline the disc, while the undead tissue is located between the yellow dotted lines. Hemocytes are labeled with nuclear hmlΔRFP marker (red) [50] and JNK activity is shown by puc-lacZ staining (white). Activated hemocytes are present as single cells (white arrow), while inactive hemocytes form cell clusters in the antennal portion of the disc and in the posterior eye disc (red arrows). Only activated hemocytes are found directly adjacent to puc-lacZ-positive epithelial cells in undead tissue. The white arrow in (A) indicates the location where the orthogonal (YZ) section was applied, shown enlarged in (A′). Yellow arrows in (A′) highlight examples where hemocytes are adjacent to puc-lacZ-positive epithelial cells. Scale bar 50 μm.
(B–D) eiger (egr) mutants (C) and eye-specific (ey-Gal4) knockdown of grindelwald (grnd) (D) strongly suppress the overgrowth of the adult head cuticle of ey>hid-p35 animals (B). Genotype in (C): UAS-hid; egr3/egr3; ey-Gal4 UAS-p35. Scale bars 200 μm.
(E) Quantification of the suppression of overgrowth of ey>hid-p35 animals by egr3 mutants, egr RNAi, wengen (wgn) RNAi and grindelwald (grnd) RNAi. Based on qualitative screening criteria (presence of ectopic ocelli and bristles; expansion of mid-head capsule width; see Figure 1B), progeny are scored as wild type (black bars) or having an overgrowth phenotype (red bars). Suppression is determined based on a shift in the percentage to wild-type from overgrown animals that is significantly different based on a Pearson’s chi-squared test for degrees of freedom=1, χ2 = 10.83 at p=.001. For detailed statistical analysis see Figure S3H.
(F,G,H) eiger mutants suppress JNK activity in ey>hid-p35 discs. Dashed white lines outline the disc, while the undead tissue is located between the yellow dotted lines. The suppression of adult head overgrowth of ey>hid-p35 animals by egr mutants (C) correlates with loss of JNK activity (MMP1; red in F–H; grey in F′–H′; see arrows) and normalization of the ELAV pattern (blue) in ey>hid-p35 discs (compare G and H). Scale bars 50 μm.
(I) grnd RNAi suppresses JNK activity (puc-lacZ) in undead tissue (between yellow dotted lines, see arrow in I′) suggesting that Grnd is required for JNK activation. The suppression of adult head overgrowth by Grnd RNAi correlates with normalization of the ELAV pattern (magenta) in ey>hid-p35 tissue. CC3 (green) labeling is present, but reduced, in ey>hid-p35; Grnd RNAi discs. Scale bar 50 μm.