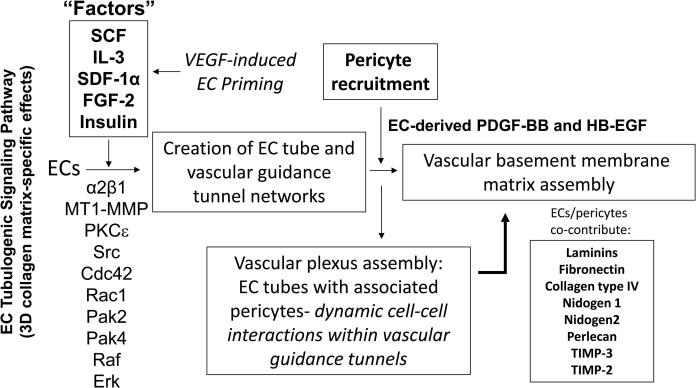
Figure 7. Molecular control of human capillary tube morphogenesis and maturation in 3D matrices.
Schematic diagram showing key molecular regulators of EC tubulogenesis and pericyte recruitment to EC tubes which control capillary network formation and maturation. Dynamic and polarized EC-pericyte interactions within vascular guidance tunnels results in abluminal vascular basement membrane matrix assembly. EC tubulogenesis is driven by growth factor-dependent signals secondary to a special combination of five growth factors (“Factors”) which are SCF, IL-3, SDF-1α, FGF-2 and Insulin. VEGF can prime ECs in an upstream step to facilitate their responsiveness to the “Factors”. These “Factors” stimulate an integrin-, MT1-MMP-, and Rho GTPase-dependent signaling cascade which controls the development of EC tube networks and vascular guidance tunnels in 3D matrices. These networks produce PDGF-BB and HB-EGF to induce recruitment and proliferation of pericytes and together ECs and pericytes co-assemble within tunnel spaces to co-contribute and deposit the vascular basement membrane along the abluminal EC tube surface in between the two cell types.