Figure 2.
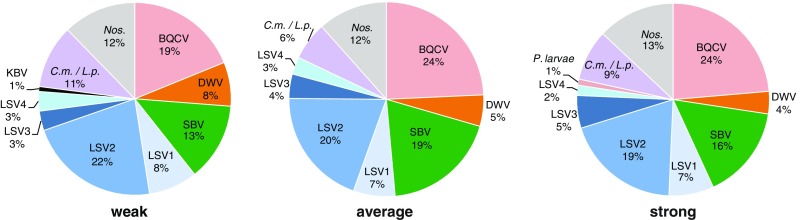
Distribution of honey bee pathogens detected in weak, average, and strong colonies. Honey bee samples were obtained from monitor colonies from October 2013 to June 2014. PCR was used to test for 16 honey bee-infecting pathogens including viruses (ABPV, BQCV, CBPV, DWV, IAPV, KBV, SBV, LSV1, LSV2, LSV3, LSV4, and LSV5, microsporidia (N. ceranae), bacteria (P. larvae and M. plutonius), and trypanosomatids (C.m./L.p.). The pathogen occurrence in weak (<5 frames; n = 41), average (six to eight frames), or strong (>9 frames; n = 81) honey bee colonies is shown as a percentage of the total number of pathogens detected by PCR. The percent pathogen occurrence for each colony strength rating is as follows: weak (BQCV 19 %, DWV 8 %, SBV 13 %, LSV1 8 %, LSV2 22 %, LSV3 3 %, LSV4 3 %, KBV 1 %, C.m./L.p. 11 %, N. ceranae 12 %), average (BQCV 24 %, DWV 5 %, SBV 19 %, LSV1 7 %, LSV2 20 %, LSV3 4 %, LSV4 3 %, C.m./L.p. 6 %, N. ceranae 12 %), and strong (BQCV 24 %, DWV 4 %, SBV 16 %, LSV1 7 %, LSV2 19 %, LSV3 5 %, LSV4 2 %, P. larvae 1 %, C.m./L.p. 9 %, N. ceranae 13 %).
