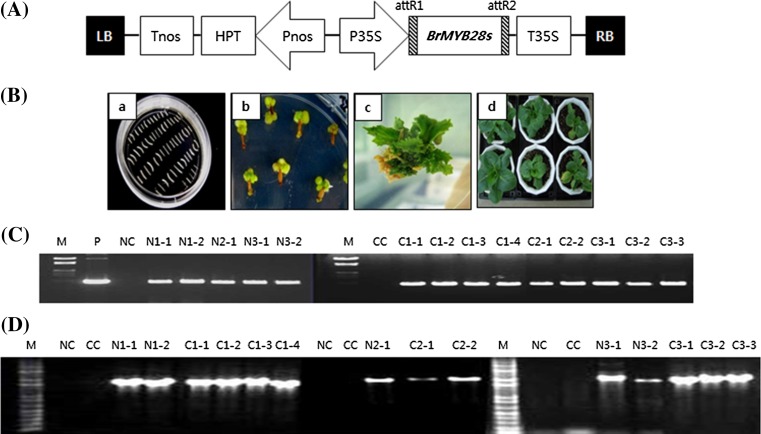
Fig. 4.
Schematic diagram of part of the T-DNA region of the binary vector and PCR analysis of transgenic Chinese cabbage. A T-DNA region of binary vector construct used for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. LB, left border; RB, right border; 35S Pro, CaMV 35S promoter; Pnos, Nos promoter; Tnos, Nos terminator, HPT, hygromycin resistance gene. B Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of BrMYB28 genes in Chinese cabbage. a Hypocotyl explants of B. rapa used for transformation. b Hygromycin-resistant callus induced from hypocotyl in selection medium containing 10 mg/L hygromycin. c Hygromycin resistance shoot regenerated from callus in regeneration medium containing 10 mg/L hygromycin. d The hygromycin-resistant plantlets were transferred to soil in pots and grown to maturity in a greenhouse with non-transgenic plants (leftmost panel). C, D Detection of the hpt gene (C) and the three BrMYB28 genes (D) in hygromycin-resistant plants (T1) by PCR analysis. The PCR products were identified at 757 bp for the hpt gene and 1454 bp for BrMYB28.1, 1581 bp for BrMYB28.2, and 1821 bp for BrMYB28.3. M, molecular weight marker; P, plasmid DNA; NC, CC, nontransgenic NW line (NC) and CT001 line (CC); N1-1,2, NW BrMYB28.1 gene transgenic plants; N2-1, NW BrMYB28.2 gene transgenic plant; N3-1,2, NW BrMYB28.3 gene transgenic plants; C1-1–4, CT001 BrMYB28.1 gene transgenic plants; C2-1–2; CT001 BrMYB28.2 gene transgenic plants; C3-1–3, CT001 BrMYB28.3 gene transgenic plants