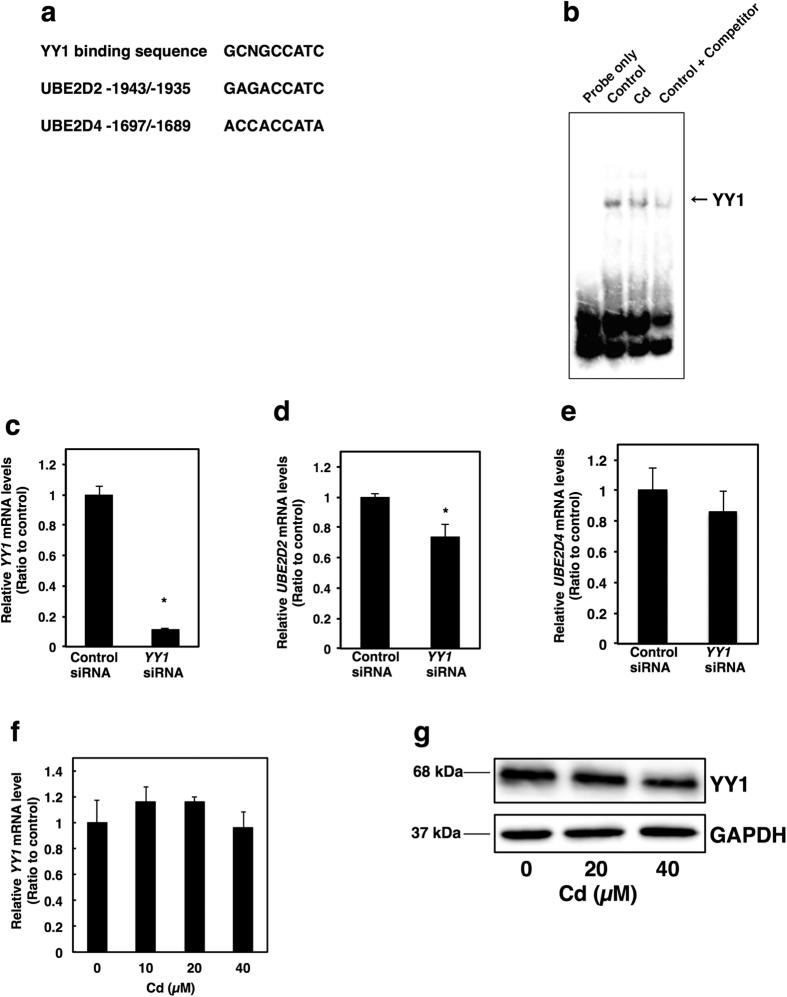
Figure 3. YY1 transcription factor is involved in Cd-induced suppression of UBE2D2 gene expression in HK-2 cells.
(a) High accuracy between the YY1 binding site and sequences upstream of UBE2D2 and UBE2D4 gene regions. Nucleotide abbreviation in the YY1 binding sequence is as follows: N is any nucleotide. (b) DNA binding activity of YY1 transcription factor in Cd-treated cells. (c) Knockdown efficiency of the YY1 gene in HK-2 cells by YY1 siRNA treatment. YY1 siRNA was added to HK-2 cells for 24 h. (d,e) mRNA levels of UBE2D2 and UBE2D4 in HK-2 cells treated with YY1 siRNA. YY1 siRNA was added to HK-2 cells for 24 h. (f) Real-time RT-PCR of YY1 gene expression. HK-2 cells were grown in six-well plates at a density of 2.0 × 104 cells/cm2 and cultured for 48 h. Culture medium was discarded and the cells were treated with Cd (CdCl2) in serum-free culture medium for 3 h. (c–f) mRNA levels were examined using real-time RT-PCR. Values are the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH. *Significantly different from the control group, P < 0.05. (g) Western blot analysis of YY1 in HK-2 cells after treatment with Cd for 3 h. Anti-GAPDH antibody was used as a loading control. Upper panel, YY1; lower panel, GAPDH. The two blots were run under the same experimental conditions. Uncropped images are provided in Supplementary Fig. 1d.