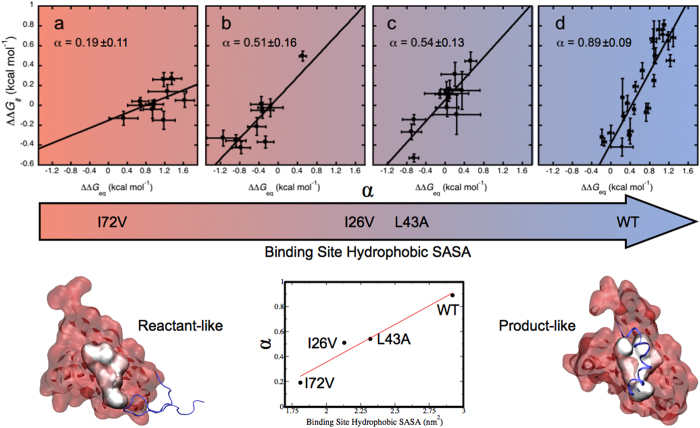
Figure 2. Unexpected variability of the KIX-c-Myb binding process.
We used the LFER approach to analyse the binding of variants I26V, L43A and I72V of KIX to the different variants of c-Myb. (a–d) The slope obtained from a linear fit of each ΔΔGeq vs ΔΔG# plot yields the α value, reflecting the native-like structure observed in the reaction transition state and varying from 0 (reactant like) to 1 (product-like). Errors on α values have been estimated using a bootstrap analysis. The structure of the transition state for the reactant-like mutant I72V and for wild type KIX are shown for comparison. A scatter plot between the α value and the hydrophobic accessible surface area calculated using the hydrophobic residues in the binding site of each KIX variant is shown in the middle between the two structures. As described in the text, the observed linear correlation suggests the folding of c-Myb to occur via heterogeneous nucleation process templated by the structure of KIX.