Figure 3. Differential behavioral responses of cntnap2ab mutants to psychoactive agents.
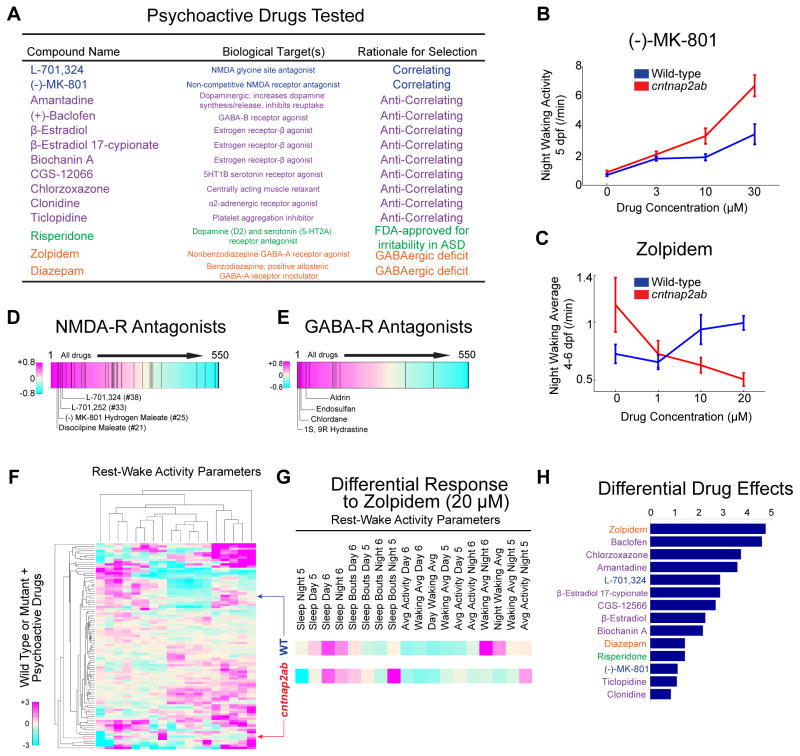
A. The 14 psychoactive drugs tested in cntnap2aΔ121/Δ121cntnap2b31i/31i and wild-type larvae, their biological targets, and the rationale for their selection. The following classes of drugs are shown: correlating (blue); anti-correlating (purple); drugs interacting with the GABA-A receptor (orange); and risperidone (green).
B, C. Dose-response effects of the NMDA receptor antagonist, (−)-MK-801, on night waking activity at 5 dpf (B) and the non-benzodiazepine GABA-A receptor agonist, zolpidem, on average night waking activity at 4–6 dpf (C) in wild-type (WT, blue) and cntnap2ab (red) larvae (p=0.002, (−)-MK-801; p=0.0003, zolpidem; two-way ANOVA, genotype x drug interaction).
D, E. Significant enrichment of NMDA receptor antagonists (D) and GABA receptor antagonists (E) in the top ranks of correlating drugs (p=0.031, NMDA-R antagonists and p=0.034, GABA-R antagonists; Kolmogorov-Smirnov).
F. Hierarchical clustering of the behavioral profiles of wild-type or cntnap2ab larvae exposed to 14 psychoactive agents at three doses each. Each rectangle in the clustergram represents the Z-score relative to the behavior of wild-type or mutant larvae exposed to DMSO alone (magenta, higher than DMSO; cyan, lower than DMSO).
G. Magnified sections highlight the behavioral fingerprints of wild-type and cntnap2ab larvae in response to zolpidem (20 μM).
H. Pairwise Euclidean distances between wild-type and cntnap2ab responses to psychoactive agents in the PCA. Note that zolpidem and (±)-baclofen produce the strongest differential responses.