Fig. 3.
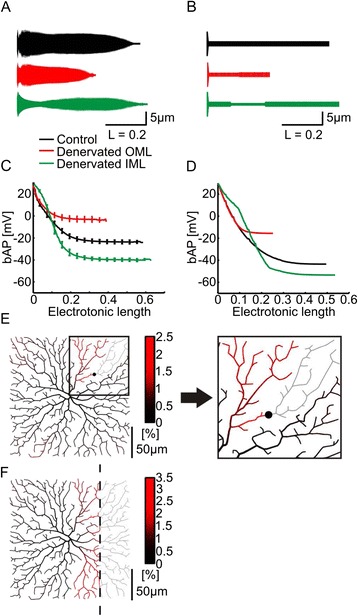
Reduced cable models and morphological models to illustrate the general principle for bAP enhancement. a Profiles (radius vs. electrotonic length) of equivalent cable models generated from synthetic cells shown in Fig. 2a (black – control; red – OML lesion; green – IML lesion). The radius of the unbranched equivalent cable was calculated from the radius of dendritic segments at a given electrotonic distance from soma (see Methods). The larger the number of branches at a given electrotonic length, the larger the radius of the equivalent cable. b Toy models for all three conditions. c, d Simulated action potential backpropagation (bAP) is plotted for the equivalent cables (c , n = 15, each; see a) and toy models (d, n = 1, each; see b) as a function of their electrotonic length. e Difference in voltage ratio (%) between lesioned and non-lesioned morphological model grown in a square dendritic field. The lesioned branch is indicated with a black dot and grey dendritic structure. Inset shows magnified region of the dendrite at which the lesion was made. f Similar to e but a large region was lesioned. The lesion is indicated with a dashed line and grey dendritic structure
