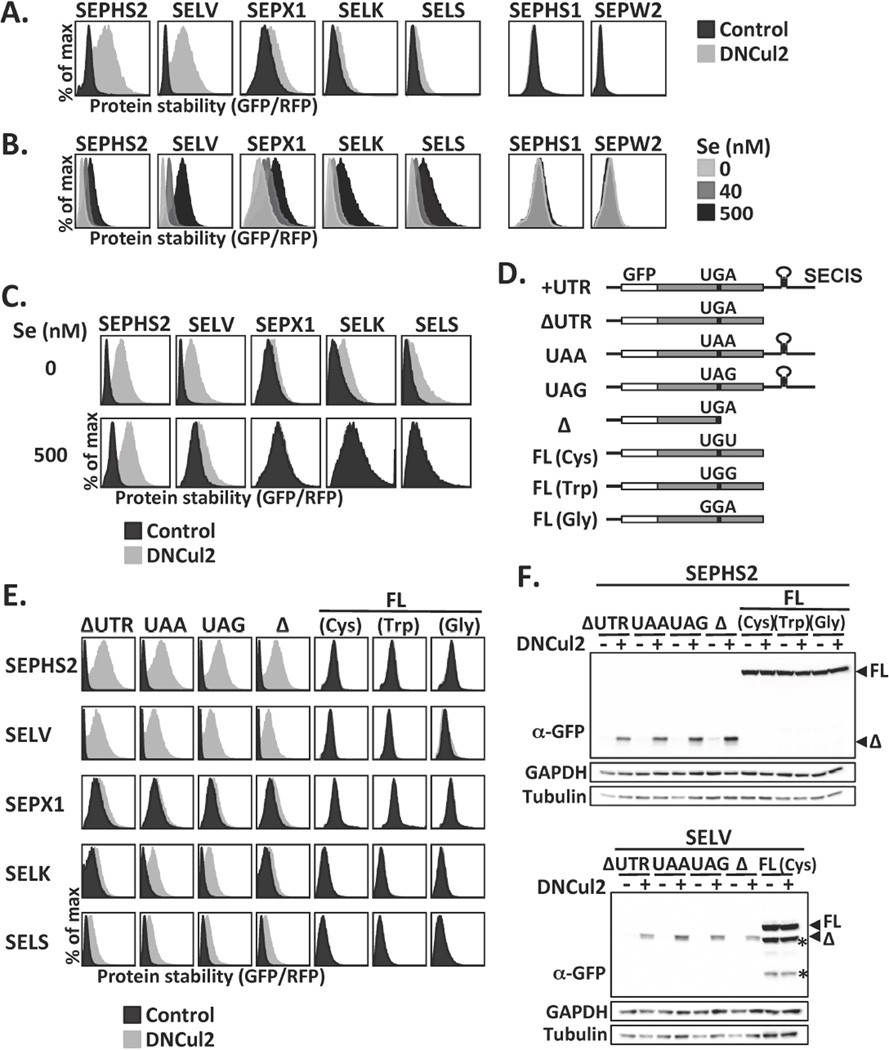
Figure 1.
Selenoprotein degradation by CRL2. (A) HEK293T GPS reporter cells expressing selenoproteins from the UTR construct were treated or not treated with dominant-negative Cul2 (DNCul2), and then analyzed. (B) GPS assay for cells cultured in serum-free medium supplemented with various concentrations of sodium selenite. (C) GPS assay for cells cultured in serum-free medium with or without sodium selenite supplement and DNCul2 treatment. (D) A schematic representation and nomenclature of each selenoprotein mutant construct. (E) GPS analysis of selenoprotein mutants in (D). Full-length and truncated selenoproteins are presented using different x-axis scales to avoid off-scaling. (F) Western blot analysis of SEPHS2 or SELV mutants. Full-length (FL) and truncated (Δ) selenoproteins are indicated by arrowheads. Asterisks mark degradation products from full-length SELV. GAPDH and tubulin were loading controls.