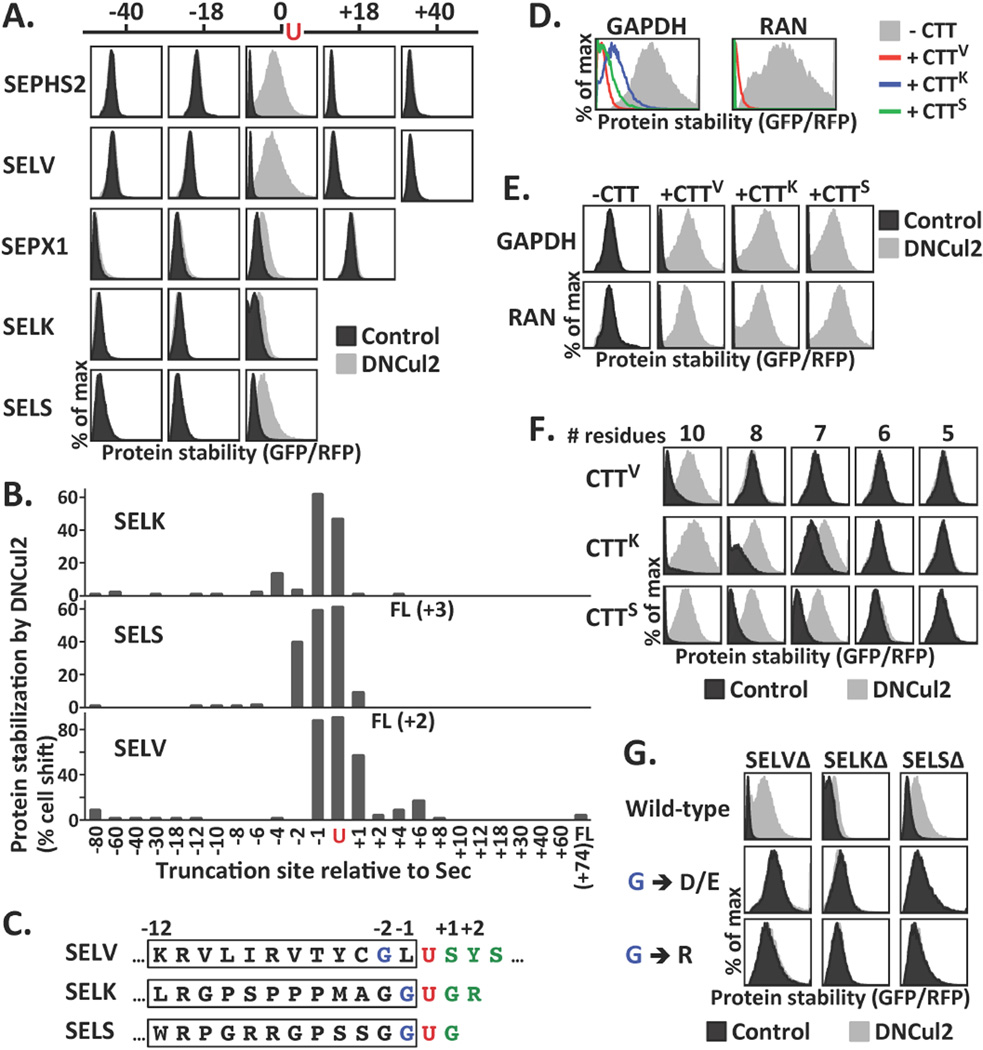
Figure 3.
Identification of the determinants for CRL2-mediated selenoprotein degradation. (A) Selenoproteins of various lengths were compared for their stability upon DNCul2 treatment. The truncation site relative to Sec is labeled above. Constructs expressing proteins longer than UGA-terminated proteins carried a UGA-to-UGU mutation. Because the stability varied dramatically among proteins, the plots were scale-adjusted for optimal resolution. The GFP/RFP ratios from separate plots cannot be compared directly. (B) By GPS assay, stabilization of selenoproteins truncated at various locations after DNCul2 treatment was quantified. (C) The sequences near Sec in SELV, SELK and SELS. The Sec, its N-terminal glycine, and C-terminal residues are labeled in red, blue and green, respectively. The 12-residue C-terminal tail (CTT) is marked with a box. (D–E) The protein stability of GAPDH or RAN without or with CTT tags at the C-terminus was analyzed. CTTV, CTTK, CTTS represent the CTT of SELVΔ, SELKΔ and SELSΔ, respectively. (F) The stability of GAPDH tagged with various lengths of CTTs. (G) The stability of UGA-terminated selenoproteins with mutations in the glycine N-terminal to Sec.