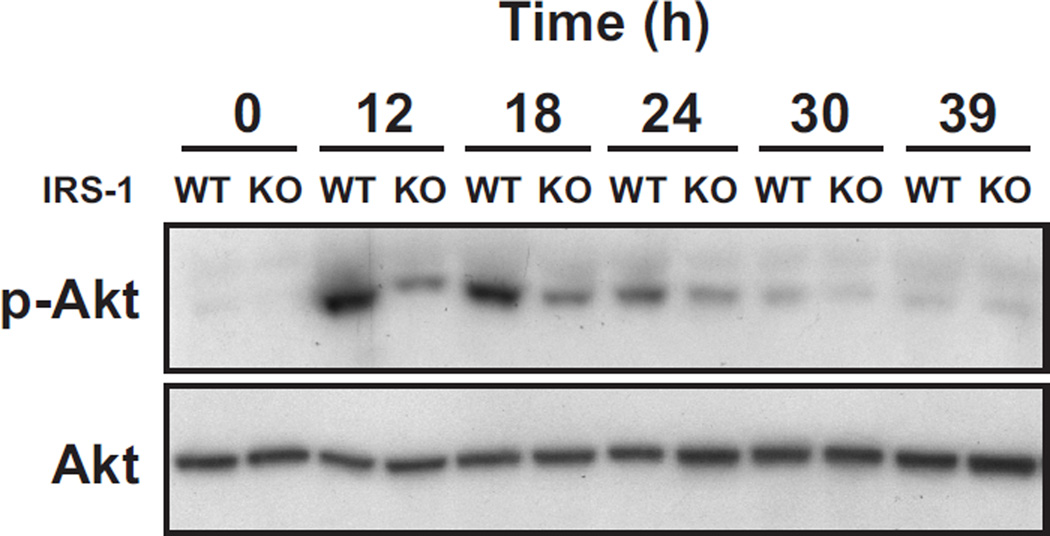
Fig. 5. Akt phosphorylation in the uterine epithelium of estradiol-treated wild-type mice and irs1−/− (KO) mice.
Ovariectomized wild-type (WT) and irs1−/− (KO) mice were treated with estradiol and uterine epithelial extracts obtained at the times indicated. Mice at the 0 time point did not receive hormone. Each lane represents analyses of one uterus. Equal amounts of extracted protein (300–400 µg) were used for WT and KO mice in each experiment. Akt was immunoprecipitated from extracts with 5 µg anti-Akt antibody and immunoblots made with antiphospho-Akt (Ser 473) and anti-Akt antibodies. Further details are given in Materials and Methods. The results shown are representative of four separate trials with different animals. The known increase in mouse uterine Akt transcripts in response to estradiol (Hewitt et al. 2003) probably accounts for the increase in Akt immunoreactivity observed at 24, 30, and 39 h.
The relative amounts (p-Akt/Akt) for KO/WT as determined by densitometry for the 12, 18, and 24 h time points of this experiment were 0.4, 0.5, and 0.4, respectively.