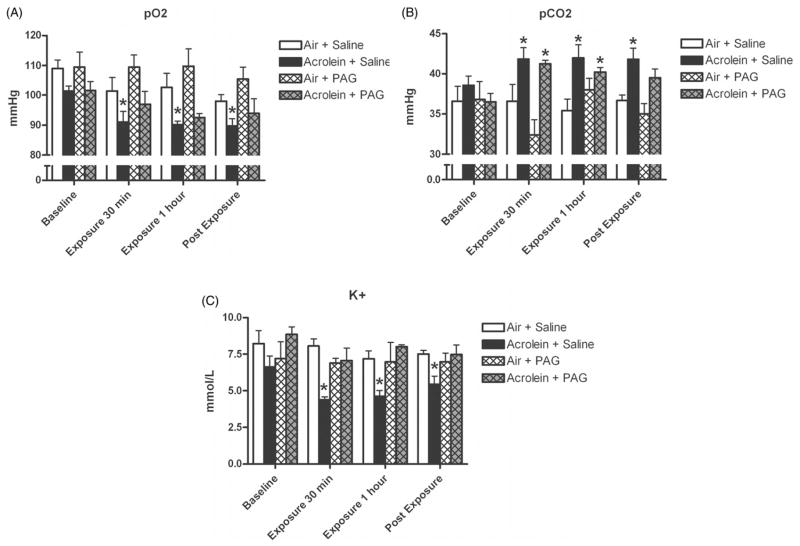
Figure 1.
Acrolein exposure causes significant decreases in arterial blood oxygen and potassium, and significant increases in arterial carbon dioxide. SH rats implanted with femoral artery catheters were injected with saline or PAG carotid body inhibitor, and exposed to 3 ppm acrolein or air control. Panels A, B and C refer to pO2, pCO2 and K+, respectively, measured at baseline, 30 min into acrolein exposure, 1 h into acrolein exposure and 15 min post-exposure. Means and standard errors are reported. Significant differences from baseline values (p<0.05) are denoted with an asterisk.