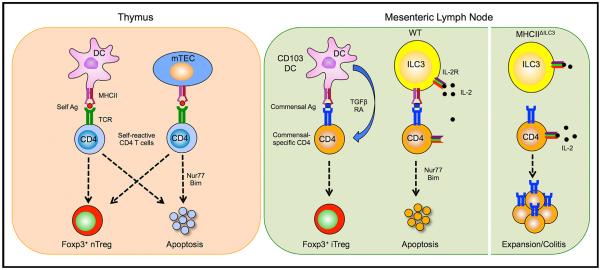
Figure 1. Selection of Self-Reactive and Commensal-Specific CD4 T Cells.
(Left) In the thymus, bone marrow-derived APCs, such as DCs, and mTECs eliminate self-reactive CD4 T cells either through the induction of apoptosis during negative selection or re-direction to the Treg cell lineage.
(Right) In the MLN, activated commensal-specific CD4 T cells are either directed to the Treg cell lineage by CD103+ DCs or deleted through induction of apoptosis by MHCII+ ILC3s in a process of “intestinal selection.” ILC3s induce apoptosis by IL-2 withdrawal, which activates Nur77 and the proapoptotic factor Bim. Conditional deletion of MHCII on ILC3 (MHCIIΔILC3 mice) prevents deletion and leads to expansion of commensal-specific CD4 T cells, which results in intestinal inflammation in the presence of appropriate microbiota.