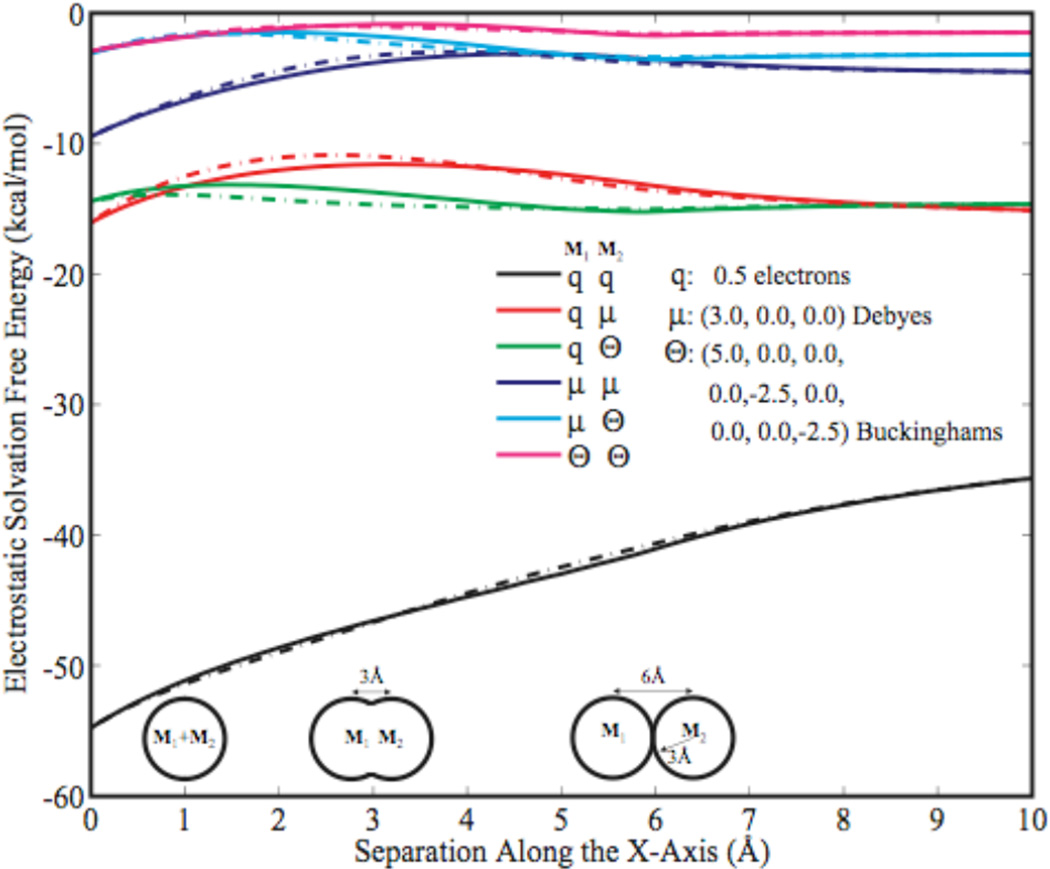
Figure 1.
The solvation energy for a system composed two spheres, each with a radius of 3 Å and permittivity of 1, and a variety of multipole combinations are computed as a function of separation along the x-axis using numerical Poisson solutions (solid lines) and generalized Kirkwood (dashed lines). The solvent permittivity was 78.3. The limiting cases of wide separation and superimposition are reproduced in all cases, while intermediate separations are seen to be a reasonable approximation.