Figure 1.
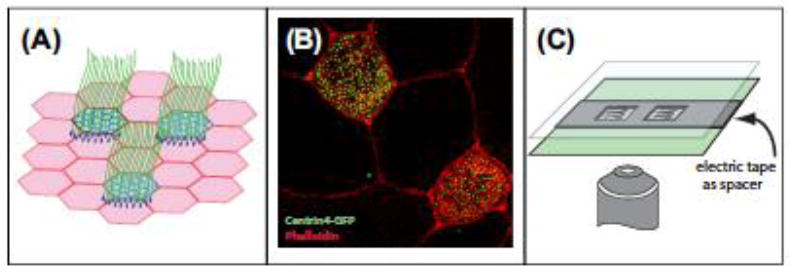
Xenopus MCCs.
(A) Illustration of the ciliated epithelia that covers the skin of Xenopus embryos. (B) Confocal image of multiciliated cells with centrin4-GFP marking centrioles/basal bodies (green) and rhodamine-phalloidin marking actin in the cell periphery (red). (C) Illustration of the mounting of Xenopus embryos using electrical tape as a spacer.
