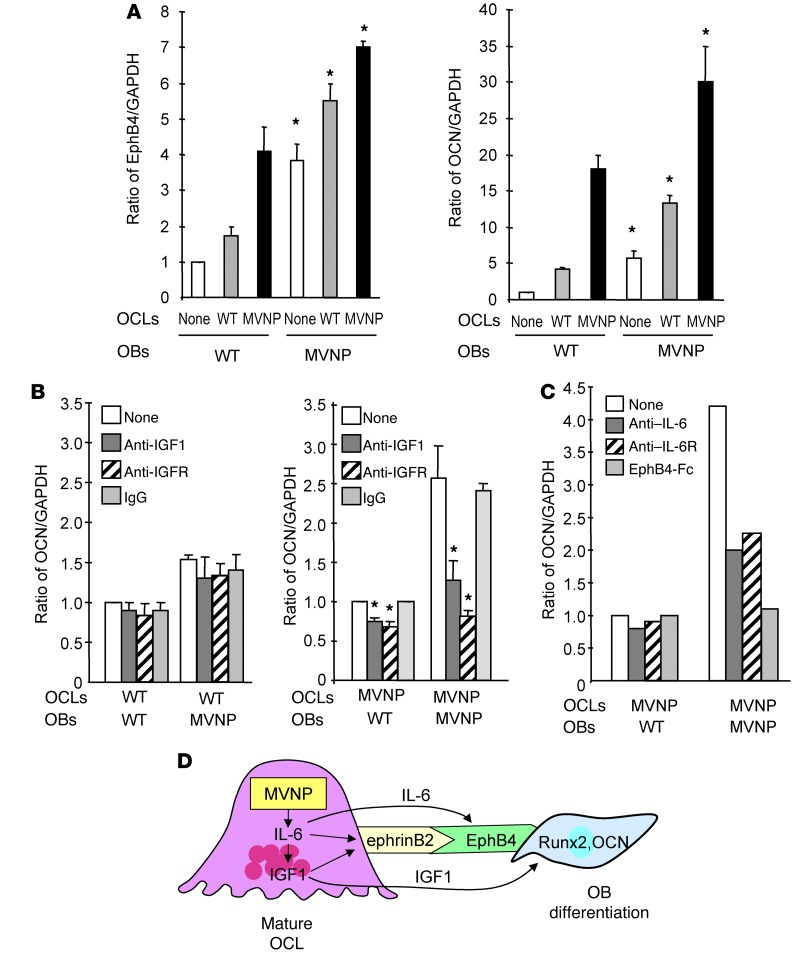
Figure 7. EphB4 and OCN expression in OBs cocultured with OCLs from WT or MVNP mice.
(A) OCLs (2.5 × 104/well) derived from MVNP or WT OCL precursors were cultured overnight with 50 ng/ml RANKL. OBs (1 × 105/well), then plated on top of the OCLs and the cells cocultured for 72 hours. Lysates were tested for EphB4 and OCN expression. Data represent the mean ± SD for 3 biological replicates. *P < 0.01 compared with cocultures with WT OCLs using a 2-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test. (B) OCLs formed by WT or MVNP OCL precursors were prepared and cocultured with OBs for 72 hours as described in Figure 5A in the presence of anti-IGF1 (10 ng/ml), anti-IGF1R (0.5 μg/ml), or rabbit IgG (20 ng/ml), then assayed for OCN expression. The relative ratios of OCN/GAPDH were measured by ImageJ software. Data represent the mean ± SD for 3 biological replicates. *P < 0.01 compared with cultures with control IgG using a 2-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test. (C) OCLs formed by MVNP OCL precursors were cocultured with OBs for 72 hours (as described in Figure 5A) with anti–IL-6 (0.5 μg/ml), anti–IL-6R (0.5 μg/ml), or EphB4-Fc (5 μg/ml), then assayed for OCN expression. The relative ratios of OCN/GAPDH were measured by ImageJ software. Data are from a representative experiment of 2 biological replicates. (D) Model of OCL-OB coupling in PD: MVNP induces high IL-6 expression in OCLs, which increases expression of IGF1 and ephrinB2 in OCLs and EphB4 on OBs to enhance coupling. IGF1 enhances ephrinB2 expression on OCLs and increases Runx2 and OCN levels in OBs to increase bone formation.