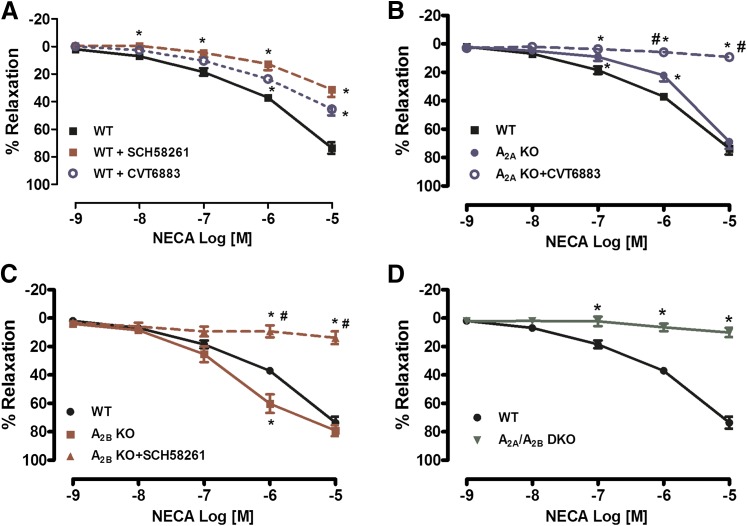
Fig. 1.
Adenosine receptor (AR)-mediated relaxation in the pudendal artery (PA) is mediated through activation of both the A2AAR and A2BAR. (A) NECA induced a concentration- dependent relaxation, and treatment with either an A2AAR antagonist (SCH-58261; 1 μM) or A2BAR antagonist (CVT-6883; 1 μM) resulted in a decrease in NECA-mediated vasorelaxation. (B) Genetic deletion of the A2AAR resulted in a decrease in NECA-mediated relaxation compared with wild type (WT), and treatment with an A2BAR antagonist (CVT-6883) completely abolished the NECA response. (C) Genetic deletion of the A2BAR resulted in significantly altered NECA-mediated relaxation compared with WT, and treatment with an A2AAR antagonist (SCH-58261) abolished the NECA response. (D) In A2A/A2BAR DKO mice, the vasorelaxation response to the adenosine receptor agonist NECA was completely abolished. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. (N = 5–7). *P < 0.05 versus WT and #P < 0.05 versus corresponding KO (A2AAR KO or A2BAR KO).