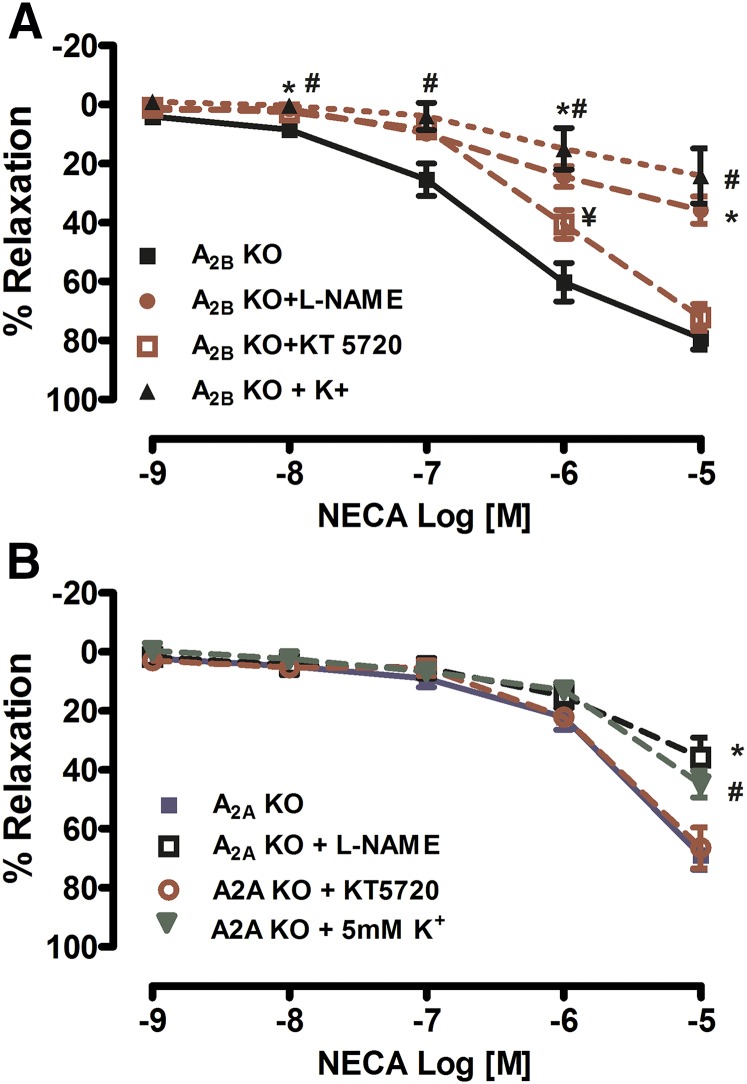
Fig. 5.
Both A2AAR- and A2BAR-mediated vasorelaxation is dependent on nitric oxide (NO) in PAs. (A) Treatment with a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor (L-NAME; 100 μM), increased K+ (5 mM KCl), or with a protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor (KT 5720; 0.1 μM) significantly decreased A2AAR-mediated vasorelaxation from A2BAR KO mice. (B) Treatment with the either the NOS inhibitor or increased K+ significantly decreased the A2BAR-mediated vasorelaxation, whereas treatment with KT 5720 (0.1 μM) did not affect relaxation in A2AAR KO mice. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. (N = 4–7). *P < 0.05 L-NAME versus vehicle, #P < 0.05 K+ versus vehicle and ¥P < 0.05 KT5720 versus vehicle.